大型語言模型(llm)已經(jīng)徹底改變了自然語言處理領(lǐng)域。隨著這些模型在規(guī)模和復(fù)雜性上的增長,推理的計(jì)算需求也顯著增加。為了應(yīng)對(duì)這一挑戰(zhàn)利用多個(gè)gpu變得至關(guān)重要。
所以本文將在多個(gè)gpu上并行執(zhí)行推理,主要包括:Accelerate庫介紹,簡(jiǎn)單的方法與工作代碼示例和使用多個(gè)gpu的性能基準(zhǔn)測(cè)試。
本文將使用多個(gè)3090將llama2-7b的推理擴(kuò)展在多個(gè)GPU上
基本示例
我們首先介紹一個(gè)簡(jiǎn)單的示例來演示使用Accelerate進(jìn)行多gpu“消息傳遞”。
from accelerate import Accelerator
from accelerate.utils import gather_object
accelerator = Accelerator()
# each GPU creates a string
message=[ f"Hello this is GPU {accelerator.process_index}" ]
# collect the messages from all GPUs
messages=gather_object(message)
# output the messages only on the main process with accelerator.print()
accelerator.print(messages)
輸出如下:
['Hello this is GPU 0',
'Hello this is GPU 1',
'Hello this is GPU 2',
'Hello this is GPU 3',
'Hello this is GPU 4']
多GPU推理
下面是一個(gè)簡(jiǎn)單的、非批處理的推理方法。代碼很簡(jiǎn)單,因?yàn)锳ccelerate庫已經(jīng)幫我們做了很多工作,我們直接使用就可以:
from accelerate import Accelerator
from accelerate.utils import gather_object
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
from statistics import mean
import torch, time, json
accelerator = Accelerator()
# 10*10 Prompts. Source: https://www.penguin.co.uk/articles/2022/04/best-first-lines-in-books
prompts_all=[
"The King is dead. Long live the Queen.",
"Once there were four children whose names were Peter, Susan, Edmund, and Lucy.",
"The story so far: in the beginning, the universe was created.",
"It was a bright cold day in April, and the clocks were striking thirteen.",
"It is a truth universally acknowledged, that a single man in possession of a good fortune, must be in want of a wife.",
"The sweat wis lashing oafay Sick Boy; he wis trembling.",
"124 was spiteful. Full of Baby's venom.",
"As Gregor Samsa awoke one morning from uneasy dreams he found himself transformed in his bed into a gigantic insect.",
"I write this sitting in the kitchen sink.",
"We were somewhere around Barstow on the edge of the desert when the drugs began to take hold.",
] * 10
# load a base model and tokenizer
model_path="models/llama2-7b"
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
model_path,
device_map={"": accelerator.process_index},
torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16,
)
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_path)
# sync GPUs and start the timer
accelerator.wait_for_everyone()
start=time.time()
# divide the prompt list onto the available GPUs
with accelerator.split_between_processes(prompts_all) as prompts:
# store output of generations in dict
results=dict(outputs=[], num_tokens=0)
# have each GPU do inference, prompt by prompt
for prompt in prompts:
prompt_tokenized=tokenizer(prompt, return_tensors="pt").to("cuda")
output_tokenized = model.generate(**prompt_tokenized, max_new_tokens=100)[0]
# remove prompt from output
output_tokenized=output_tokenized[len(prompt_tokenized["input_ids"][0]):]
# store outputs and number of tokens in result{}
results["outputs"].append( tokenizer.decode(output_tokenized) )
results["num_tokens"] += len(output_tokenized)
results=[ results ] # transform to list, otherwise gather_object() will not collect correctly
# collect results from all the GPUs
results_gathered=gather_object(results)
if accelerator.is_main_process:
timediff=time.time()-start
num_tokens=sum([r["num_tokens"] for r in results_gathered ])
print(f"tokens/sec: {num_tokens//timediff}, time {timediff}, total tokens {num_tokens}, total prompts {len(prompts_all)}")
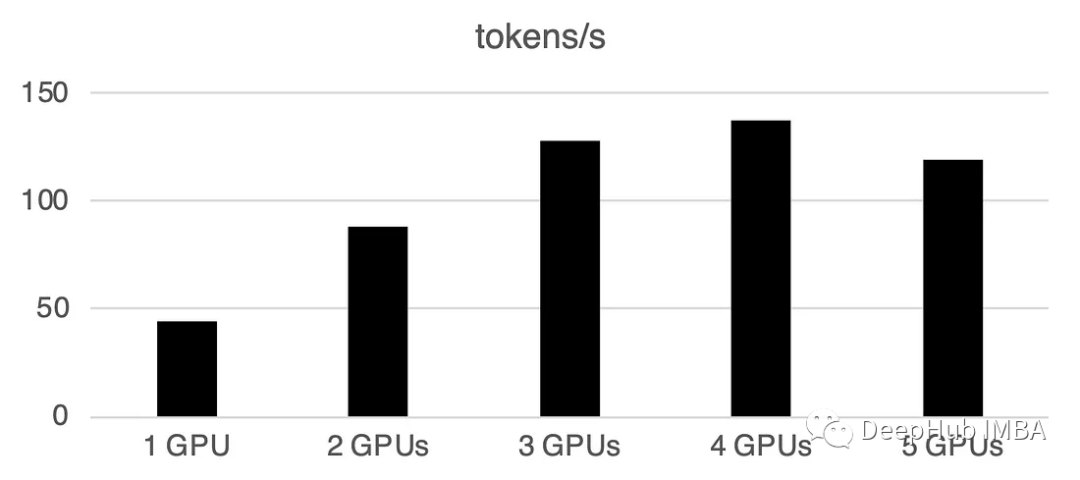
使用多個(gè)gpu會(huì)導(dǎo)致一些通信開銷:性能在4個(gè)gpu時(shí)呈線性增長,然后在這種特定設(shè)置中趨于穩(wěn)定。當(dāng)然這里的性能取決于許多參數(shù),如模型大小和量化、提示長度、生成的令牌數(shù)量和采樣策略,所以我們只討論一般的情況
1 GPU: 44個(gè)token /秒,時(shí)間:225.5s
2 gpu: 88個(gè)token /秒,時(shí)間:112.9s
3 gpu: 128個(gè)token /秒,時(shí)間:77.6s
4 gpu: 137個(gè)token /秒,時(shí)間:72.7s
5 gpu: 119個(gè)token /秒,時(shí)間:83.8s
在多GPU上進(jìn)行批處理
現(xiàn)實(shí)世界中,我們可以使用批處理推理來加快速度。這會(huì)減少GPU之間的通訊,加快推理速度。我們只需要增加prepare_prompts函數(shù)將一批數(shù)據(jù)而不是單條數(shù)據(jù)輸入到模型即可:
from accelerate import Accelerator
from accelerate.utils import gather_object
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
from statistics import mean
import torch, time, json
accelerator = Accelerator()
def write_pretty_json(file_path, data):
import json
with open(file_path, "w") as write_file:
json.dump(data, write_file, indent=4)
# 10*10 Prompts. Source: https://www.penguin.co.uk/articles/2022/04/best-first-lines-in-books
prompts_all=[
"The King is dead. Long live the Queen.",
"Once there were four children whose names were Peter, Susan, Edmund, and Lucy.",
"The story so far: in the beginning, the universe was created.",
"It was a bright cold day in April, and the clocks were striking thirteen.",
"It is a truth universally acknowledged, that a single man in possession of a good fortune, must be in want of a wife.",
"The sweat wis lashing oafay Sick Boy; he wis trembling.",
"124 was spiteful. Full of Baby's venom.",
"As Gregor Samsa awoke one morning from uneasy dreams he found himself transformed in his bed into a gigantic insect.",
"I write this sitting in the kitchen sink.",
"We were somewhere around Barstow on the edge of the desert when the drugs began to take hold.",
] * 10
# load a base model and tokenizer
model_path="models/llama2-7b"
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
model_path,
device_map={"": accelerator.process_index},
torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16,
)
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_path)
tokenizer.pad_token = tokenizer.eos_token
# batch, left pad (for inference), and tokenize
def prepare_prompts(prompts, tokenizer, batch_size=16):
batches=[prompts[i:i + batch_size] for i in range(0, len(prompts), batch_size)]
batches_tok=[]
tokenizer.padding_side="left"
for prompt_batch in batches:
batches_tok.append(
tokenizer(
prompt_batch,
return_tensors="pt",
padding='longest',
truncation=False,
pad_to_multiple_of=8,
add_special_tokens=False).to("cuda")
)
tokenizer.padding_side="right"
return batches_tok
# sync GPUs and start the timer
accelerator.wait_for_everyone()
start=time.time()
# divide the prompt list onto the available GPUs
with accelerator.split_between_processes(prompts_all) as prompts:
results=dict(outputs=[], num_tokens=0)
# have each GPU do inference in batches
prompt_batches=prepare_prompts(prompts, tokenizer, batch_size=16)
for prompts_tokenized in prompt_batches:
outputs_tokenized=model.generate(**prompts_tokenized, max_new_tokens=100)
# remove prompt from gen. tokens
outputs_tokenized=[ tok_out[len(tok_in):]
for tok_in, tok_out in zip(prompts_tokenized["input_ids"], outputs_tokenized) ]
# count and decode gen. tokens
num_tokens=sum([ len(t) for t in outputs_tokenized ])
outputs=tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs_tokenized)
# store in results{} to be gathered by accelerate
results["outputs"].extend(outputs)
results["num_tokens"] += num_tokens
results=[ results ] # transform to list, otherwise gather_object() will not collect correctly
# collect results from all the GPUs
results_gathered=gather_object(results)
if accelerator.is_main_process:
timediff=time.time()-start
num_tokens=sum([r["num_tokens"] for r in results_gathered ])
print(f"tokens/sec: {num_tokens//timediff}, time elapsed: {timediff}, num_tokens {num_tokens}")
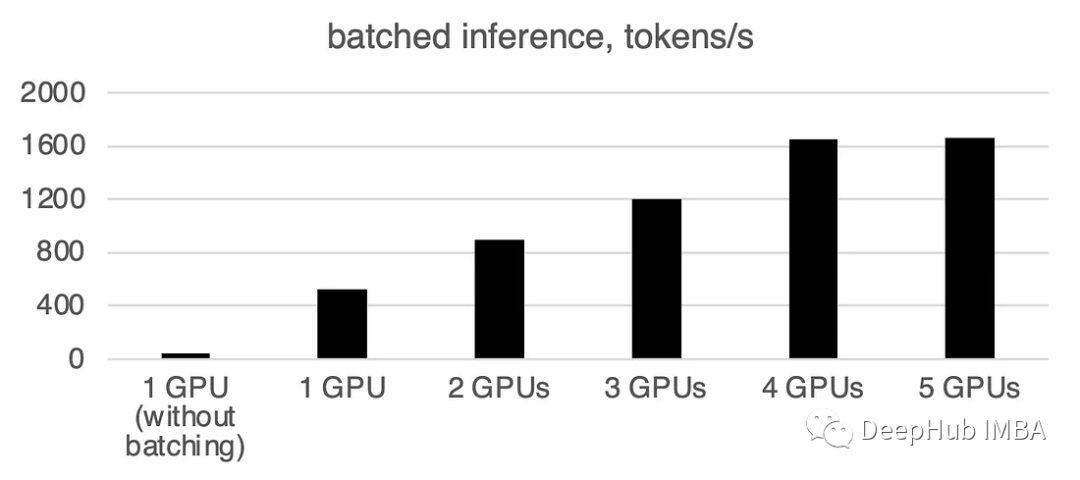
可以看到批處理會(huì)大大加快速度。
1 GPU: 520 token /sec,時(shí)間:19.2s
2 gpu: 900 token /sec,時(shí)間:11.1s
3 gpu: 1205個(gè)token /秒,時(shí)間:8.2s
4 gpu: 1655 token /sec,時(shí)間:6.0s
5 gpu: 1658 token /sec,時(shí)間:6.0s
總結(jié)
截止到本文為止,llama.cpp,ctransformer還不支持多GPU推理,好像llama.cpp在6月有個(gè)多GPU的merge,但是我沒看到官方更新,所以這里暫時(shí)確定不支持多GPU。如果有小伙伴確認(rèn)可以支持多GPU請(qǐng)留言。
huggingface的Accelerate包則為我們使用多GPU提供了一個(gè)很方便的選擇,使用多個(gè)GPU推理可以顯著提高性能,但gpu之間通信的開銷隨著gpu數(shù)量的增加而顯著增加。
-
GPU芯片
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
1文章
305瀏覽量
6120 -
自然語言處理
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
1文章
628瀏覽量
14008 -
LLM
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
1文章
319瀏覽量
680
發(fā)布評(píng)論請(qǐng)先 登錄
【飛凌嵌入式OK3576-C開發(fā)板體驗(yàn)】rkllm板端推理
YOLOv5s算法在RK3399ProD上的部署推理流程是怎樣的
怎樣在阿里云物聯(lián)網(wǎng)平臺(tái)上進(jìn)行單片機(jī)程序的編寫呢
充分利用Arm NN進(jìn)行GPU推理
如何判斷推理何時(shí)由GPU或NPU在iMX8MPlus上運(yùn)行?
使用Devtron在Kubernetes多集群上進(jìn)行開發(fā)
PyTorch教程13.5之在多個(gè)GPU上進(jìn)行訓(xùn)練

Nvidia 通過開源庫提升 LLM 推理性能
現(xiàn)已公開發(fā)布!歡迎使用 NVIDIA TensorRT-LLM 優(yōu)化大語言模型推理

Hugging Face LLM部署大語言模型到亞馬遜云科技Amazon SageMaker推理示例
利用NVIDIA組件提升GPU推理的吞吐
LLM大模型推理加速的關(guān)鍵技術(shù)
解鎖NVIDIA TensorRT-LLM的卓越性能
大模型訓(xùn)練框架(五)之Accelerate
詳解 LLM 推理模型的現(xiàn)狀






 怎樣使用Accelerate庫在多GPU上進(jìn)行LLM推理呢?
怎樣使用Accelerate庫在多GPU上進(jìn)行LLM推理呢?










評(píng)論