CompletableFuture是jdk8的新特性。CompletableFuture實(shí)現(xiàn)了CompletionStage接口和Future接口,前者是對(duì)后者的一個(gè)擴(kuò)展,增加了異步會(huì)點(diǎn)、流式處理、多個(gè)Future組合處理的能力,使Java在處理多任務(wù)的協(xié)同工作時(shí)更加順暢便利。
一、創(chuàng)建異步任務(wù)
1. supplyAsync
supplyAsync是創(chuàng)建帶有返回值的異步任務(wù)。它有如下兩個(gè)方法,一個(gè)是使用默認(rèn)線程池(ForkJoinPool.commonPool())的方法,一個(gè)是帶有自定義線程池的重載方法
//帶返回值異步請(qǐng)求,默認(rèn)線程池
publicstaticCompletableFuturesupplyAsync(Suppliersupplier)
//帶返回值的異步請(qǐng)求,可以自定義線程池
publicstaticCompletableFuturesupplyAsync(Suppliersupplier,Executorexecutor)
測(cè)試代碼:
publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args)throwsExecutionException,InterruptedException{
CompletableFuturecf=CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
System.out.println("dosomething....");
return"result";
});
//等待任務(wù)執(zhí)行完成
System.out.println("結(jié)果->"+cf.get());
}
publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args)throwsExecutionException,InterruptedException{
//自定義線程池
ExecutorServiceexecutorService=Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
CompletableFuturecf=CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
System.out.println("dosomething....");
return"result";
},executorService);
//等待子任務(wù)執(zhí)行完成
System.out.println("結(jié)果->"+cf.get());
}
測(cè)試結(jié)果:
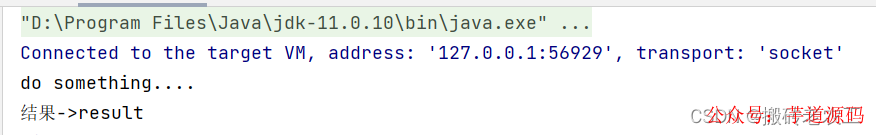
2. runAsync
runAsync是創(chuàng)建沒有返回值的異步任務(wù)。它有如下兩個(gè)方法,一個(gè)是使用默認(rèn)線程池(ForkJoinPool.commonPool())的方法,一個(gè)是帶有自定義線程池的重載方法
//不帶返回值的異步請(qǐng)求,默認(rèn)線程池
publicstaticCompletableFuturerunAsync(Runnablerunnable)
//不帶返回值的異步請(qǐng)求,可以自定義線程池
publicstaticCompletableFuturerunAsync(Runnablerunnable,Executorexecutor)
測(cè)試代碼:
publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args)throwsExecutionException,InterruptedException{
CompletableFuturecf=CompletableFuture.runAsync(()->{
System.out.println("dosomething....");
});
//等待任務(wù)執(zhí)行完成
System.out.println("結(jié)果->"+cf.get());
}
publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args)throwsExecutionException,InterruptedException{
//自定義線程池
ExecutorServiceexecutorService=Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
CompletableFuturecf=CompletableFuture.runAsync(()->{
System.out.println("dosomething....");
},executorService);
//等待任務(wù)執(zhí)行完成
System.out.println("結(jié)果->"+cf.get());
}
測(cè)試結(jié)果:
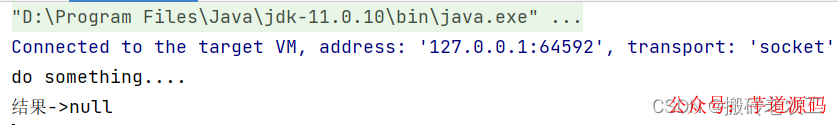
3.獲取任務(wù)結(jié)果的方法
//如果完成則返回結(jié)果,否則就拋出具體的異常
publicTget()throwsInterruptedException,ExecutionException
//最大時(shí)間等待返回結(jié)果,否則就拋出具體異常
publicTget(longtimeout,TimeUnitunit)throwsInterruptedException,ExecutionException,TimeoutException
//完成時(shí)返回結(jié)果值,否則拋出unchecked異常。為了更好地符合通用函數(shù)形式的使用,如果完成此CompletableFuture所涉及的計(jì)算引發(fā)異常,則此方法將引發(fā)unchecked異常并將底層異常作為其原因
publicTjoin()
//如果完成則返回結(jié)果值(或拋出任何遇到的異常),否則返回給定的valueIfAbsent。
publicTgetNow(TvalueIfAbsent)
//如果任務(wù)沒有完成,返回的值設(shè)置為給定值
publicbooleancomplete(Tvalue)
//如果任務(wù)沒有完成,就拋出給定異常
publicbooleancompleteExceptionally(Throwableex)
基于 Spring Boot + MyBatis Plus + Vue & Element 實(shí)現(xiàn)的后臺(tái)管理系統(tǒng) + 用戶小程序,支持 RBAC 動(dòng)態(tài)權(quán)限、多租戶、數(shù)據(jù)權(quán)限、工作流、三方登錄、支付、短信、商城等功能
- 項(xiàng)目地址:https://github.com/YunaiV/ruoyi-vue-pro
- 視頻教程:https://doc.iocoder.cn/video/
二、異步回調(diào)處理
1. thenApply和thenApplyAsync
thenApply 表示某個(gè)任務(wù)執(zhí)行完成后執(zhí)行的動(dòng)作,即回調(diào)方法,會(huì)將該任務(wù)的執(zhí)行結(jié)果即方法返回值作為入?yún)鬟f到回調(diào)方法中,帶有返回值。
測(cè)試代碼:
publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args)throwsExecutionException,InterruptedException{
CompletableFuturecf1=CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"cf1dosomething....");
return1;
});
CompletableFuturecf2=cf1.thenApplyAsync((result)->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"cf2dosomething....");
result+=2;
returnresult;
});
//等待任務(wù)1執(zhí)行完成
System.out.println("cf1結(jié)果->"+cf1.get());
//等待任務(wù)2執(zhí)行完成
System.out.println("cf2結(jié)果->"+cf2.get());
}
publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args)throwsExecutionException,InterruptedException{
CompletableFuturecf1=CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"cf1dosomething....");
return1;
});
CompletableFuturecf2=cf1.thenApply((result)->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"cf2dosomething....");
result+=2;
returnresult;
});
//等待任務(wù)1執(zhí)行完成
System.out.println("cf1結(jié)果->"+cf1.get());
//等待任務(wù)2執(zhí)行完成
System.out.println("cf2結(jié)果->"+cf2.get());
}
測(cè)試結(jié)果:
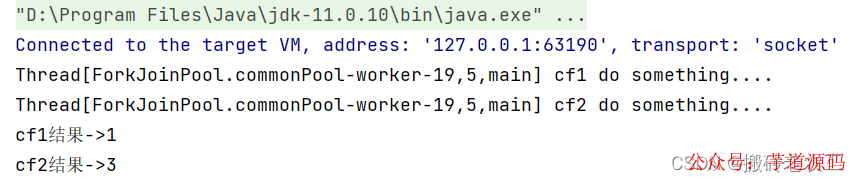
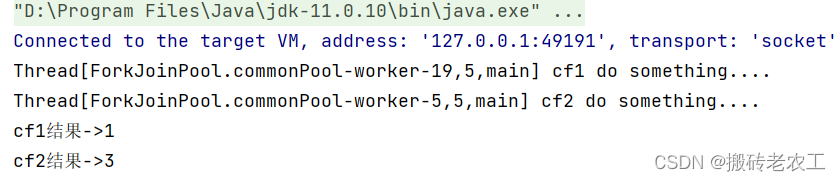
從上面代碼和測(cè)試結(jié)果我們發(fā)現(xiàn)thenApply和thenApplyAsync區(qū)別在于,使用thenApply方法時(shí)子任務(wù)與父任務(wù)使用的是同一個(gè)線程,而thenApplyAsync在子任務(wù)中是另起一個(gè)線程執(zhí)行任務(wù),并且thenApplyAsync可以自定義線程池,默認(rèn)的使用ForkJoinPool.commonPool()線程池。
2. thenAccept和thenAcceptAsync
thenAccep表示某個(gè)任務(wù)執(zhí)行完成后執(zhí)行的動(dòng)作,即回調(diào)方法,會(huì)將該任務(wù)的執(zhí)行結(jié)果即方法返回值作為入?yún)鬟f到回調(diào)方法中,無返回值。
測(cè)試代碼
publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args)throwsExecutionException,InterruptedException{
CompletableFuturecf1=CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"cf1dosomething....");
return1;
});
CompletableFuturecf2=cf1.thenAccept((result)->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"cf2dosomething....");
});
//等待任務(wù)1執(zhí)行完成
System.out.println("cf1結(jié)果->"+cf1.get());
//等待任務(wù)2執(zhí)行完成
System.out.println("cf2結(jié)果->"+cf2.get());
}
publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args)throwsExecutionException,InterruptedException{
CompletableFuturecf1=CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"cf1dosomething....");
return1;
});
CompletableFuturecf2=cf1.thenAcceptAsync((result)->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"cf2dosomething....");
});
//等待任務(wù)1執(zhí)行完成
System.out.println("cf1結(jié)果->"+cf1.get());
//等待任務(wù)2執(zhí)行完成
System.out.println("cf2結(jié)果->"+cf2.get());
}
測(cè)試結(jié)果:

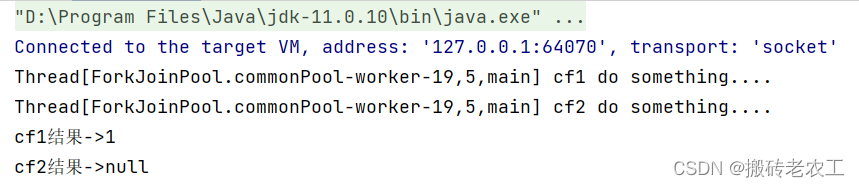 從上面代碼和測(cè)試結(jié)果我們發(fā)現(xiàn)thenAccep和thenAccepAsync區(qū)別在于,使用thenAccep方法時(shí)子任務(wù)與父任務(wù)使用的是同一個(gè)線程,而thenAccepAsync在子任務(wù)中可能是另起一個(gè)線程執(zhí)行任務(wù),并且thenAccepAsync可以自定義線程池,默認(rèn)的使用ForkJoinPool.commonPool()線程池。
從上面代碼和測(cè)試結(jié)果我們發(fā)現(xiàn)thenAccep和thenAccepAsync區(qū)別在于,使用thenAccep方法時(shí)子任務(wù)與父任務(wù)使用的是同一個(gè)線程,而thenAccepAsync在子任務(wù)中可能是另起一個(gè)線程執(zhí)行任務(wù),并且thenAccepAsync可以自定義線程池,默認(rèn)的使用ForkJoinPool.commonPool()線程池。
3.thenRun和thenRunAsync
thenRun表示某個(gè)任務(wù)執(zhí)行完成后執(zhí)行的動(dòng)作,即回調(diào)方法,無入?yún)ⅲ瑹o返回值。
測(cè)試代碼:
publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args)throwsExecutionException,InterruptedException{
CompletableFuturecf1=CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"cf1dosomething....");
return1;
});
CompletableFuturecf2=cf1.thenRun(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"cf2dosomething....");
});
//等待任務(wù)1執(zhí)行完成
System.out.println("cf1結(jié)果->"+cf1.get());
//等待任務(wù)2執(zhí)行完成
System.out.println("cf2結(jié)果->"+cf2.get());
}
publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args)throwsExecutionException,InterruptedException{
CompletableFuturecf1=CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"cf1dosomething....");
return1;
});
CompletableFuturecf2=cf1.thenRunAsync(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"cf2dosomething....");
});
//等待任務(wù)1執(zhí)行完成
System.out.println("cf1結(jié)果->"+cf1.get());
//等待任務(wù)2執(zhí)行完成
System.out.println("cf2結(jié)果->"+cf2.get());
}
測(cè)試結(jié)果:
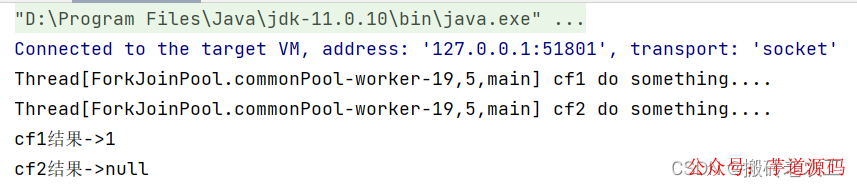
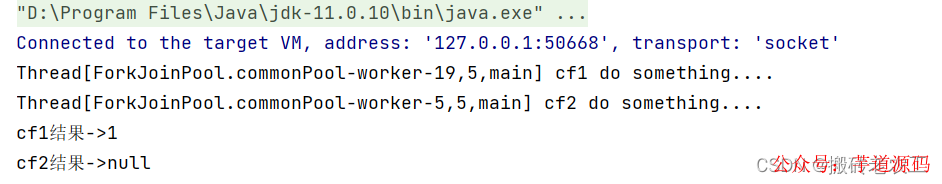
從上面代碼和測(cè)試結(jié)果我們發(fā)現(xiàn)thenRun和thenRunAsync區(qū)別在于,使用thenRun方法時(shí)子任務(wù)與父任務(wù)使用的是同一個(gè)線程,而thenRunAsync在子任務(wù)中可能是另起一個(gè)線程執(zhí)行任務(wù),并且thenRunAsync可以自定義線程池,默認(rèn)的使用ForkJoinPool.commonPool()線程池。
4.whenComplete和whenCompleteAsync
whenComplete是當(dāng)某個(gè)任務(wù)執(zhí)行完成后執(zhí)行的回調(diào)方法,會(huì)將執(zhí)行結(jié)果或者執(zhí)行期間拋出的異常傳遞給回調(diào)方法,如果是正常執(zhí)行則異常為null,回調(diào)方法對(duì)應(yīng)的CompletableFuture的result和該任務(wù)一致,如果該任務(wù)正常執(zhí)行,則get方法返回執(zhí)行結(jié)果,如果是執(zhí)行異常,則get方法拋出異常。
測(cè)試代碼:
publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args)throwsExecutionException,InterruptedException{
CompletableFuturecf1=CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"cf1dosomething....");
inta=1/0;
return1;
});
CompletableFuturecf2=cf1.whenComplete((result,e)->{
System.out.println("上個(gè)任務(wù)結(jié)果:"+result);
System.out.println("上個(gè)任務(wù)拋出異常:"+e);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"cf2dosomething....");
});
////等待任務(wù)1執(zhí)行完成
//System.out.println("cf1結(jié)果->"+cf1.get());
////等待任務(wù)2執(zhí)行完成
System.out.println("cf2結(jié)果->"+cf2.get());
}
測(cè)試結(jié)果:
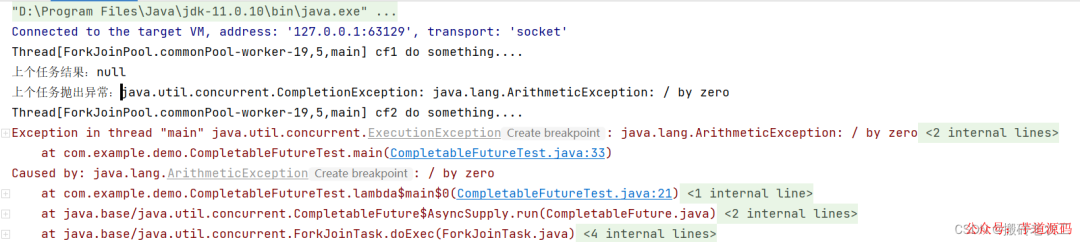
whenCompleteAsync和whenComplete區(qū)別也是whenCompleteAsync可能會(huì)另起一個(gè)線程執(zhí)行任務(wù),并且thenRunAsync可以自定義線程池,默認(rèn)的使用ForkJoinPool.commonPool()線程池。
5.handle和handleAsync
跟whenComplete基本一致,區(qū)別在于handle的回調(diào)方法有返回值。
測(cè)試代碼:
publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args)throwsExecutionException,InterruptedException{
CompletableFuturecf1=CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"cf1dosomething....");
//inta=1/0;
return1;
});
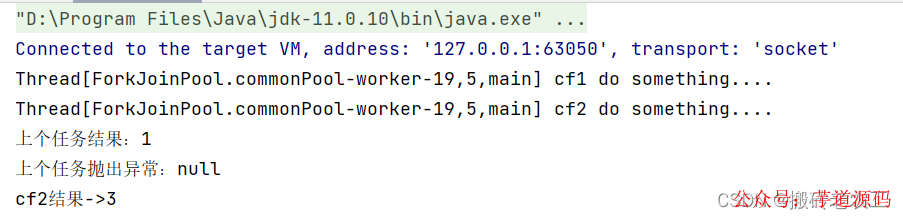
CompletableFuturecf2=cf1.handle((result,e)->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"cf2dosomething....");
System.out.println("上個(gè)任務(wù)結(jié)果:"+result);
System.out.println("上個(gè)任務(wù)拋出異常:"+e);
returnresult+2;
});
//等待任務(wù)2執(zhí)行完成
System.out.println("cf2結(jié)果->"+cf2.get());
}
測(cè)試結(jié)果 :
基于 Spring Cloud Alibaba + Gateway + Nacos + RocketMQ + Vue & Element 實(shí)現(xiàn)的后臺(tái)管理系統(tǒng) + 用戶小程序,支持 RBAC 動(dòng)態(tài)權(quán)限、多租戶、數(shù)據(jù)權(quán)限、工作流、三方登錄、支付、短信、商城等功能
三、多任務(wù)組合處理
1. thenCombine、thenAcceptBoth 和runAfterBoth
這三個(gè)方法都是將兩個(gè)CompletableFuture組合起來處理,只有兩個(gè)任務(wù)都正常完成時(shí),才進(jìn)行下階段任務(wù)。
區(qū)別:thenCombine會(huì)將兩個(gè)任務(wù)的執(zhí)行結(jié)果作為所提供函數(shù)的參數(shù),且該方法有返回值;thenAcceptBoth同樣將兩個(gè)任務(wù)的執(zhí)行結(jié)果作為方法入?yún)ⅲ菬o返回值;runAfterBoth沒有入?yún)ⅲ矝]有返回值。注意兩個(gè)任務(wù)中只要有一個(gè)執(zhí)行異常,則將該異常信息作為指定任務(wù)的執(zhí)行結(jié)果。
測(cè)試代碼:
publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args)throwsExecutionException,InterruptedException{
CompletableFuturecf1=CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"cf1dosomething....");
return1;
});
CompletableFuturecf2=CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"cf2dosomething....");
return2;
});
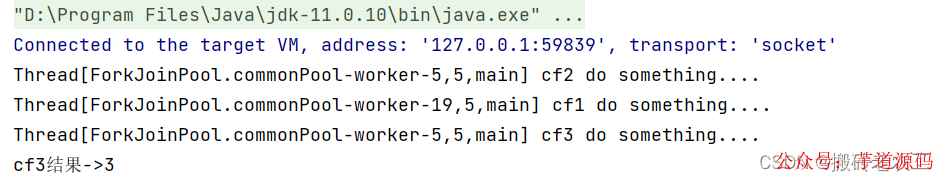
CompletableFuturecf3=cf1.thenCombine(cf2,(a,b)->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"cf3dosomething....");
returna+b;
});
System.out.println("cf3結(jié)果->"+cf3.get());
}
publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args)throwsExecutionException,InterruptedException{
CompletableFuturecf1=CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"cf1dosomething....");
return1;
});
CompletableFuturecf2=CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"cf2dosomething....");
return2;
});
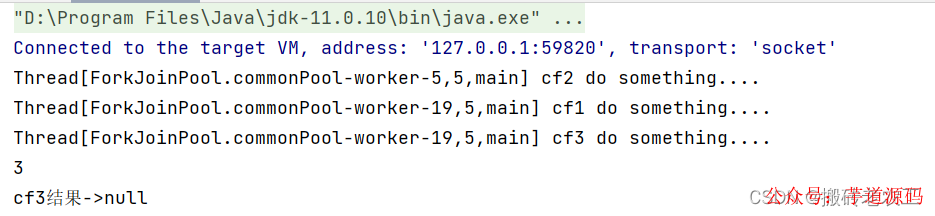
CompletableFuturecf3=cf1.thenAcceptBoth(cf2,(a,b)->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"cf3dosomething....");
System.out.println(a+b);
});
System.out.println("cf3結(jié)果->"+cf3.get());
}
publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args)throwsExecutionException,InterruptedException{
CompletableFuturecf1=CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"cf1dosomething....");
return1;
});
CompletableFuturecf2=CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"cf2dosomething....");
return2;
});
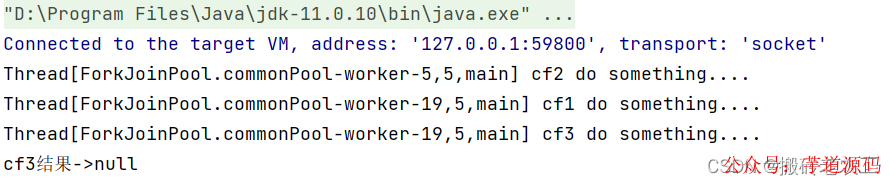
CompletableFuturecf3=cf1.runAfterBoth(cf2,()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"cf3dosomething....");
});
System.out.println("cf3結(jié)果->"+cf3.get());
}
測(cè)試結(jié)果:
 2.applyToEither、acceptEither和runAfterEither
2.applyToEither、acceptEither和runAfterEither
這三個(gè)方法和上面一樣也是將兩個(gè)CompletableFuture組合起來處理,當(dāng)有一個(gè)任務(wù)正常完成時(shí),就會(huì)進(jìn)行下階段任務(wù)。
區(qū)別:applyToEither會(huì)將已經(jīng)完成任務(wù)的執(zhí)行結(jié)果作為所提供函數(shù)的參數(shù),且該方法有返回值;acceptEither同樣將已經(jīng)完成任務(wù)的執(zhí)行結(jié)果作為方法入?yún)ⅲ菬o返回值;runAfterEither沒有入?yún)ⅲ矝]有返回值。
測(cè)試代碼:
publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args)throwsExecutionException,InterruptedException{
CompletableFuturecf1=CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
try{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"cf1dosomething....");
Thread.sleep(2000);
}catch(InterruptedExceptione){
e.printStackTrace();
}
return"cf1任務(wù)完成";
});
CompletableFuturecf2=CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
try{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"cf2dosomething....");
Thread.sleep(5000);
}catch(InterruptedExceptione){
e.printStackTrace();
}
return"cf2任務(wù)完成";
});
CompletableFuturecf3=cf1.applyToEither(cf2,(result)->{
System.out.println("接收到"+result);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"cf3dosomething....");
return"cf3任務(wù)完成";
});
System.out.println("cf3結(jié)果->"+cf3.get());
}
publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args)throwsExecutionException,InterruptedException{
CompletableFuturecf1=CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
try{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"cf1dosomething....");
Thread.sleep(2000);
}catch(InterruptedExceptione){
e.printStackTrace();
}
return"cf1任務(wù)完成";
});
CompletableFuturecf2=CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
try{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"cf2dosomething....");
Thread.sleep(5000);
}catch(InterruptedExceptione){
e.printStackTrace();
}
return"cf2任務(wù)完成";
});
CompletableFuturecf3=cf1.acceptEither(cf2,(result)->{
System.out.println("接收到"+result);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"cf3dosomething....");
});
System.out.println("cf3結(jié)果->"+cf3.get());
}
publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args)throwsExecutionException,InterruptedException{
CompletableFuturecf1=CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
try{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"cf1dosomething....");
Thread.sleep(2000);
}catch(InterruptedExceptione){
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("cf1任務(wù)完成");
return"cf1任務(wù)完成";
});
CompletableFuturecf2=CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
try{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"cf2dosomething....");
Thread.sleep(5000);
}catch(InterruptedExceptione){
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("cf2任務(wù)完成");
return"cf2任務(wù)完成";
});
CompletableFuturecf3=cf1.runAfterEither(cf2,()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"cf3dosomething....");
System.out.println("cf3任務(wù)完成");
});
System.out.println("cf3結(jié)果->"+cf3.get());
}
測(cè)試結(jié)果:
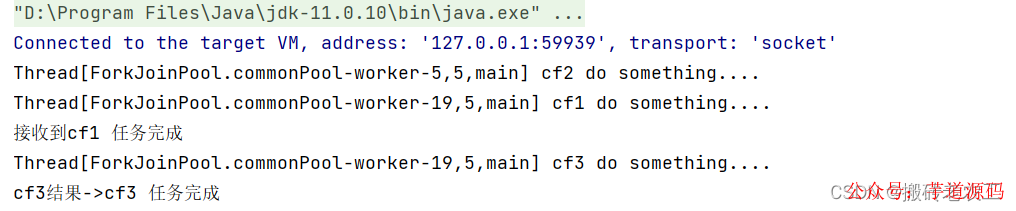
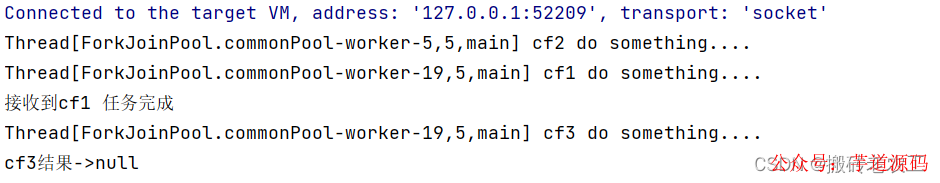
從上面可以看出cf1任務(wù)完成需要2秒,cf2任務(wù)完成需要5秒,使用applyToEither組合兩個(gè)任務(wù)時(shí),只要有其中一個(gè)任務(wù)完成時(shí),就會(huì)執(zhí)行cf3任務(wù),顯然cf1任務(wù)先完成了并且將自己任務(wù)的結(jié)果傳值給了cf3任務(wù),cf3任務(wù)中打印了接收到cf1任務(wù)完成,接著完成自己的任務(wù),并返回cf3任務(wù)完成;acceptEither和runAfterEither類似,acceptEither會(huì)將cf1任務(wù)的結(jié)果作為cf3任務(wù)的入?yún)ⅲ玞f3任務(wù)完成時(shí)并無返回值;runAfterEither不會(huì)將cf1任務(wù)的結(jié)果作為cf3任務(wù)的入?yún)ⅲ菦]有任務(wù)入?yún)ⅲ瑘?zhí)行完自己的任務(wù)后也并無返回值。
2. allOf / anyOf
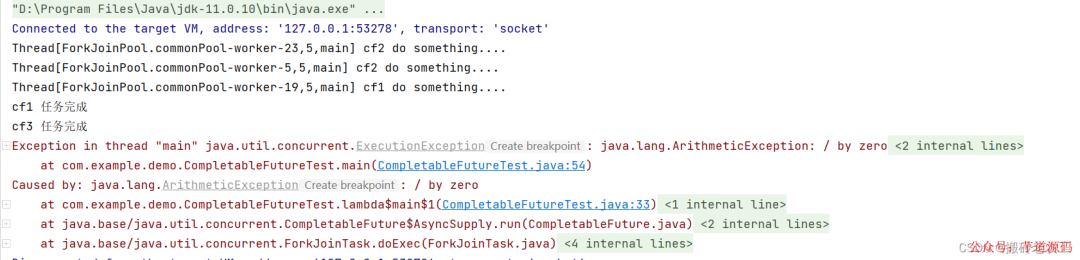
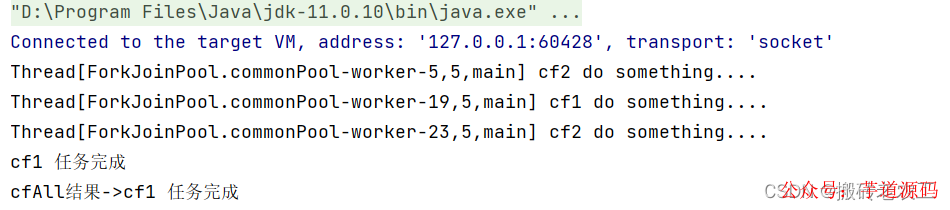
allOf:CompletableFuture是多個(gè)任務(wù)都執(zhí)行完成后才會(huì)執(zhí)行,只有有一個(gè)任務(wù)執(zhí)行異常,則返回的CompletableFuture執(zhí)行g(shù)et方法時(shí)會(huì)拋出異常,如果都是正常執(zhí)行,則get返回null。
anyOf :CompletableFuture是多個(gè)任務(wù)只要有一個(gè)任務(wù)執(zhí)行完成,則返回的CompletableFuture執(zhí)行g(shù)et方法時(shí)會(huì)拋出異常,如果都是正常執(zhí)行,則get返回執(zhí)行完成任務(wù)的結(jié)果。
測(cè)試代碼:
publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args)throwsExecutionException,InterruptedException{
CompletableFuturecf1=CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
try{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"cf1dosomething....");
Thread.sleep(2000);
}catch(InterruptedExceptione){
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("cf1任務(wù)完成");
return"cf1任務(wù)完成";
});
CompletableFuturecf2=CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
try{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"cf2dosomething....");
inta=1/0;
Thread.sleep(5000);
}catch(InterruptedExceptione){
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("cf2任務(wù)完成");
return"cf2任務(wù)完成";
});
CompletableFuturecf3=CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
try{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"cf2dosomething....");
Thread.sleep(3000);
}catch(InterruptedExceptione){
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("cf3任務(wù)完成");
return"cf3任務(wù)完成";
});
CompletableFuturecfAll=CompletableFuture.allOf(cf1,cf2,cf3);
System.out.println("cfAll結(jié)果->"+cfAll.get());
}
publicstaticvoidmain(String[]args)throwsExecutionException,InterruptedException{
CompletableFuturecf1=CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
try{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"cf1dosomething....");
Thread.sleep(2000);
}catch(InterruptedExceptione){
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("cf1任務(wù)完成");
return"cf1任務(wù)完成";
});
CompletableFuturecf2=CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
try{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"cf2dosomething....");
Thread.sleep(5000);
}catch(InterruptedExceptione){
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("cf2任務(wù)完成");
return"cf2任務(wù)完成";
});
CompletableFuturecf3=CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
try{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+"cf2dosomething....");
Thread.sleep(3000);
}catch(InterruptedExceptione){
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("cf3任務(wù)完成");
return"cf3任務(wù)完成";
});
CompletableFuture
測(cè)試結(jié)果:
審核編輯 :李倩
-
接口
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
33文章
8975瀏覽量
153518 -
線程
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
0文章
508瀏覽量
20151
原文標(biāo)題:一網(wǎng)打盡:異步神器 CompletableFuture 萬字詳解!
文章出處:【微信號(hào):芋道源碼,微信公眾號(hào):芋道源碼】歡迎添加關(guān)注!文章轉(zhuǎn)載請(qǐng)注明出處。
發(fā)布評(píng)論請(qǐng)先 登錄
【萬字長文】物聯(lián)網(wǎng)的激蕩二十年

全面解析新概念模擬電路(建議下載!)
萬字聊聊什么是智能車載終端?為什么智駕發(fā)展離不開它?
投資筆記:3萬字詳解100大新材料國產(chǎn)替代(附100+行研報(bào)告)

Xmind完成對(duì)AI總結(jié)工具Briefy的戰(zhàn)略收購
萬字長文!工業(yè)5.0的內(nèi)涵、體系架構(gòu)和使能技術(shù)

套接字socket包含哪些參數(shù)
第三篇-V1.5 TB6612電機(jī)pwm控制STM32智能小車 STM32F103C8T6單片機(jī)

第一篇:V1.5-STM32f103c8t6智能小車筆記 標(biāo)準(zhǔn)庫開發(fā) 6612電機(jī)驅(qū)動(dòng)新手入門項(xiàng)目

Java CompletableFuture 異步超時(shí)實(shí)現(xiàn)探索
FPGA異步信號(hào)處理方法
快速掌握C語言關(guān)鍵字

1.3萬字!詳解半導(dǎo)體先進(jìn)封裝行業(yè),現(xiàn)狀及發(fā)展趨勢(shì)!






 異步神器CompletableFuture萬字詳解!
異步神器CompletableFuture萬字詳解!












評(píng)論