GradientBoost算法 python實(shí)現(xiàn),該系列文章主要是對(duì)《統(tǒng)計(jì)學(xué)習(xí)方法》的實(shí)現(xiàn)。
完整的筆記和代碼以上傳到Github,地址為(覺(jué)得有用的話,歡迎Fork,請(qǐng)給作者個(gè)Star):
https://github.com/Vambooo/lihang-dl
提升樹(shù)利用加法模型與前向分步算法實(shí)現(xiàn)學(xué)習(xí)的優(yōu)化過(guò)程,當(dāng)損失函數(shù)為平方損失和指數(shù)損失函數(shù)時(shí),每一步優(yōu)化都較為簡(jiǎn)單。但對(duì)一般損失函數(shù)來(lái)說(shuō),每一步的優(yōu)化并不容易。Fredman為了解決這一問(wèn)題,便提出了梯度提升(Gradient Boosting)方法。
梯度提升法利用最速下降的近似方法,這里的關(guān)鍵是利用損失函數(shù)的負(fù)梯度在當(dāng)前模型的值r_{mi}作為回歸問(wèn)題提升樹(shù)算法中的殘差的近似值,擬合一個(gè)回歸樹(shù)。
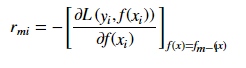
梯度提升方法(Gradient Boosting)算法
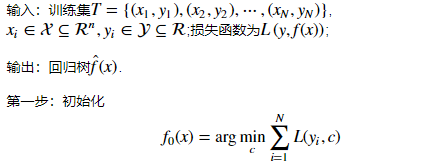
注:該步通過(guò)估計(jì)使損失函數(shù)極小化的常數(shù)值,得到一個(gè)根結(jié)點(diǎn)的樹(shù)。

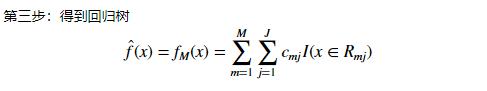
Gradient Boost算法案例 python實(shí)現(xiàn)(馬疝病數(shù)據(jù))
(代碼可以左右滑動(dòng)看)
import pandas as pdimport numpy as npimportmatplotlib.pyplotaspltfrom sklearn import ensemblefrom sklearn import linear_model
第一步:構(gòu)建數(shù)據(jù)
# 創(chuàng)建模擬數(shù)據(jù)xx = np.arange(0, 60)y=[ x / 2 + (x // 10) % 2 * 20 * x / 5 + np.random.random() * 10 for x in xx] x = pd.DataFrame({'x': x}) # Plot mock dataplt.figure(figsize=(10, 5))plt.scatter(x, y)plt.show()
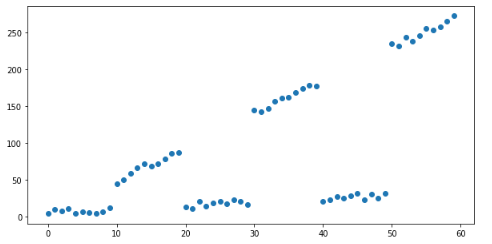
線性回歸模型來(lái)擬合數(shù)據(jù)
linear_regressor=linear_model.LinearRegression()linear_regressor.fit(x, y) plt.figure(figsize=(10, 5))plt.title("Linear Regression")plt.scatter(x, y)plt.plot(x, linear_regressor.predict(x), color='r')plt.show()
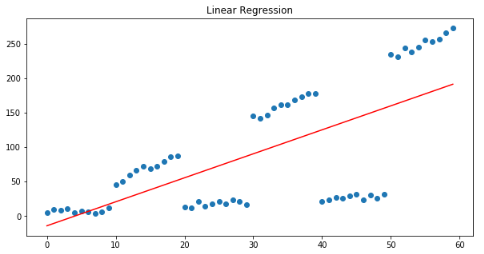
線性回歸模型旨在將預(yù)測(cè)與實(shí)際產(chǎn)出之間的平方誤差最小化,從我們的殘差模式可以清楚地看出,殘差之和約為0:
梯度提升法使用一組串聯(lián)的決策樹(shù)來(lái)預(yù)測(cè)y
下面從只有一個(gè)估計(jì)量的梯度提升回歸模型和一個(gè)只有深度為1的樹(shù)開(kāi)始:
params = { 'n_estimators': 1, 'max_depth': 1, 'learning_rate': 1, 'criterion': 'mse'}
gradient_boosting_regressor = ensemble.GradientBoostingRegressor(**params)
gradient_boosting_regressor.fit(x, y)
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 5))plt.title('Gradient Boosting model (1 estimators, Single tree split)')plt.scatter(x, y)plt.plot(x, gradient_boosting_regressor.predict(x), color='r')plt.show()
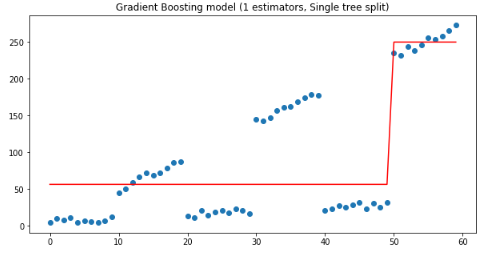
從上圖可以看到深度1決策樹(shù)在x<50??和x>50處被拆分,其中:
if x<50 ,y=56;
if x>=50,y=250.
這樣的拆分結(jié)果肯定是不好的,下面用一個(gè)估計(jì)量時(shí),30-40之間的殘差很。猜想:如果使用兩個(gè)估計(jì)量,把第一棵樹(shù)的殘差輸入下一棵樹(shù)中,有怎樣的效果?驗(yàn)證代碼如下:
params['n_estimators'] = 2
gradient_boosting_regressor = ensemble.GradientBoostingRegressor(**params)
gradient_boosting_regressor.fit(x, y)
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 5))plt.title('Gradient Boosting model (1 estimators, Single tree split)')plt.scatter(x, y)plt.plot(x, gradient_boosting_regressor.predict(x), color='r')plt.show()
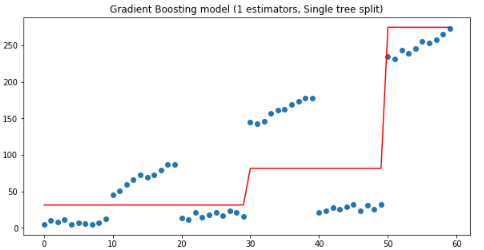
如上圖,當(dāng)有連個(gè)估計(jì)量時(shí),第二棵樹(shù)是在30處拆分的,如果我們繼續(xù)增加估計(jì)量,我們得到Y(jié)分布的一個(gè)越來(lái)越接近的近似值:
f, ax = plt.subplots(2, 2, figsize=(15, 10)) for idx, n_estimators in enumerate([5, 10, 20, 50]): params['n_estimators'] = n_estimators gradient_boosting_regressor = ensemble.GradientBoostingRegressor(**params) gradient_boosting_regressor.fit(x, y) subplot = ax[idx // 2][idx % 2] subplot.set_title('Gradient Boosting model ({} estimators, Single tree split)'.format(n_estimators)) subplot.scatter(x, y) subplot.plot(x, gradient_boosting_regressor.predict(x), color='r')plt.show()
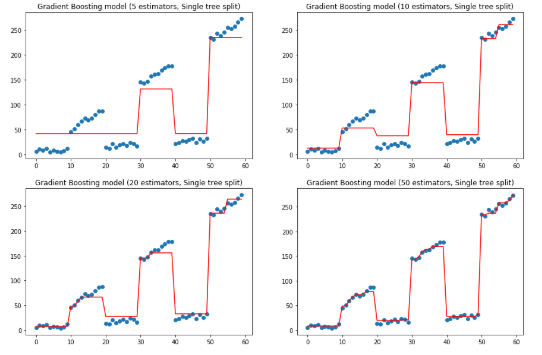
上面是改變估計(jì)量,保持樹(shù)深度的效果,下面保持估計(jì)量為10,改變樹(shù)的深度.
params['n_estimators'] = 10
f, ax = plt.subplots(2, 2, figsize=(15, 10))
for idx, max_depth in enumerate([1, 2, 3, 5]): params['max_depth'] = max_depth
gradient_boosting_regressor = ensemble.GradientBoostingRegressor(**params)
gradient_boosting_regressor.fit(x, y) subplot = ax[idx // 2][idx % 2] subplot.set_title('Gradient Boosting model (10 estimators, {} max tree splits)'.format(max_depth)) subplot.scatter(x, y) subplot.plot(x, gradient_boosting_regressor.predict(x), color='r')plt.show()
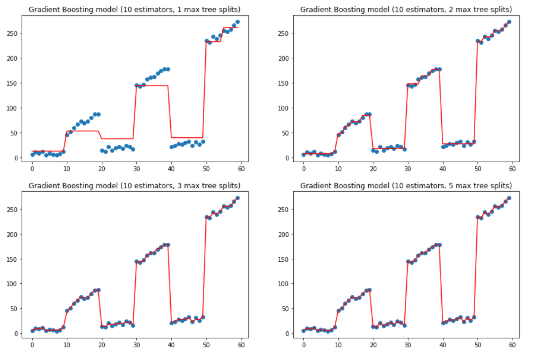
上兩圖可以看到如何通過(guò)增加估計(jì)量和最大深度來(lái)擬合y值。不過(guò)有點(diǎn)過(guò)擬合了。
-
算法
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
23文章
4698瀏覽量
94719 -
python
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
56文章
4825瀏覽量
86163
原文標(biāo)題:機(jī)器學(xué)習(xí)筆記系列(十三) | GradientBoost算法 python實(shí)現(xiàn)
文章出處:【微信號(hào):AI_class_vip,微信公眾號(hào):人工智能學(xué)研社】歡迎添加關(guān)注!文章轉(zhuǎn)載請(qǐng)注明出處。
發(fā)布評(píng)論請(qǐng)先 登錄
《MATLAB優(yōu)化算法案例分析與應(yīng)用》
機(jī)器學(xué)習(xí)新手必學(xué)的三種優(yōu)化算法(牛頓法、梯度下降法、最速下降法)
集成學(xué)習(xí)和Boosting提升方法
基礎(chǔ)算法案例
一種改進(jìn)的梯度投影算法
機(jī)器學(xué)習(xí):隨機(jī)梯度下降和批量梯度下降算法介紹
一文看懂常用的梯度下降算法
改進(jìn)深度學(xué)習(xí)算法的光伏出力預(yù)測(cè)方法
GBDT算法原理以及實(shí)例理解
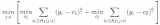
將淺層神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)作為“弱學(xué)習(xí)者”的梯度Boosting框架






 梯度提升方法(Gradient Boosting)算法案例
梯度提升方法(Gradient Boosting)算法案例











評(píng)論