本文原文地址:?https://bbs.elecfans.com/jishu_2489798_1_1.html??
作者:@jf_07365693
樹莓派RP2350 - 桌面動(dòng)態(tài)溫濕度計(jì)
本文介紹了DFrobotBeetle RP2350 開發(fā)板結(jié)合 DHT11 模塊、鋰電池模塊、隨機(jī)眨眼動(dòng)畫,實(shí)現(xiàn) OLED 顯示的桌面動(dòng)態(tài)溫濕度計(jì)的項(xiàng)目設(shè)計(jì)。
一、項(xiàng)目介紹
本項(xiàng)目包括
工程調(diào)試:電量獲取、電量圖標(biāo)顯示、DHT11 溫濕度顯示、OLED 眨眼動(dòng)畫
工程代碼:合并調(diào)試代碼,實(shí)現(xiàn)完整的項(xiàng)目設(shè)計(jì)功能
效果演示:幀動(dòng)畫顯示、動(dòng)態(tài)展示
最終實(shí)現(xiàn)桌面動(dòng)態(tài)溫濕度計(jì)的制作。
工作原理
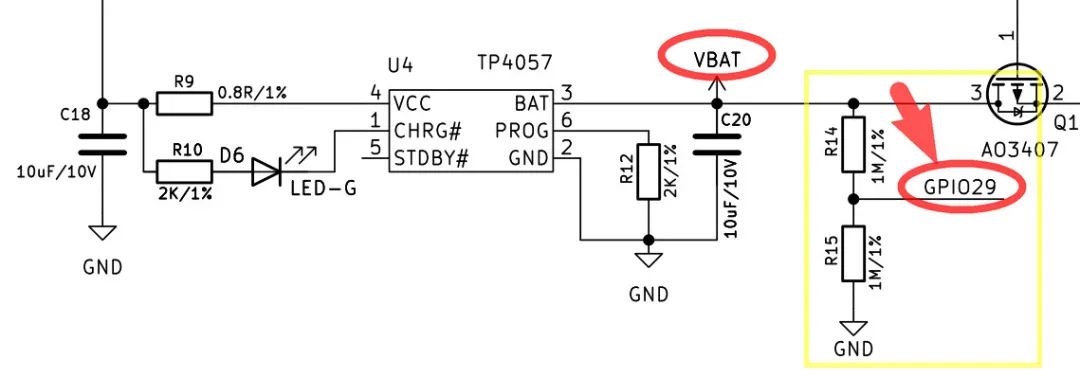
根據(jù)開發(fā)板原理圖可知,電池 VBAT 的分壓電路與主控的 GPIO29 模擬接口相連,因此通過該引腳可實(shí)時(shí)采集監(jiān)測(cè)電池電壓信息,進(jìn)而實(shí)現(xiàn)電量顯示。
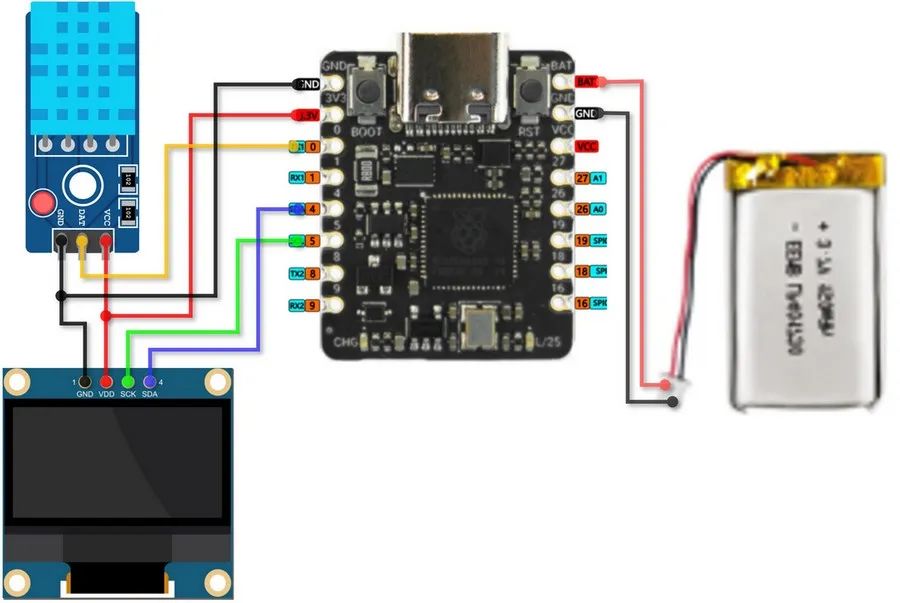
二、硬件連接
GP0 -> DATA (DHT11)
GP4 -> SDA (OLED)
GP5 -> SCL (OLED)
BAT -> Battery Positive
GND -> Battery Negative
示意圖
三、工程調(diào)試
包括 ADC 電量采集、電量的 OLED 顯示、DHT11溫濕度數(shù)據(jù)和電量圖標(biāo)的顯示、眨眼動(dòng)畫等調(diào)試項(xiàng)目。
1. 電量獲取
通過 ADC 讀取 GPIO29 電壓值并終端打印
代碼
from machine import Pin, ADC
import utime
# initialize ADC pin
adc = ADC(Pin(29))
# parameters for voltage divide resistor
R1, R2 = 1000000, 1000000
DIV_RATIO = (R1 + R2) / R1
def get_battery_level():
adc_value = adc.read_u16()
voltage = (adc_value / 65535) * 3.3
actual_voltage = voltage * DIV_RATIO # voltage division compensation
percent = min(max((actual_voltage - 3.3) / (4.2 - 3.3) * 100, 0), 100)
return percent, actual_voltage
while True:
percent, voltage = get_battery_level()
print('Battery Voltage: {:.2f} V, Battery Level: {:.1f}%'.format(voltage,percent))
utime.sleep(1)
保存代碼,連接開發(fā)板,配置解釋器并運(yùn)行。
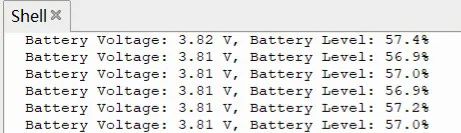
效果
終端打印 ADC 采集的電池電壓值以及電量百分比
2. 電量顯示
OLED 顯示 ADC 采集的電量百分比。
代碼
from machine import Pin, ADC, I2C
import ssd1306
import utime
# initialize ADC pin
adc = ADC(Pin(29))
# initialize OLED
i2c = I2C(0, scl=Pin(5), sda=Pin(4))
oled = ssd1306.SSD1306_I2C(128, 64, i2c)
# parameters of voltage divide resistor
R1, R2 = 1000000, 1000000 # 1M
Vref_BAT = 3.9 # battery voltage in full charged state
def get_battery_level():
adc_value = adc.read_u16()
voltage = (adc_value / 65535) * 3.3
DIV_RATIO = (R1 + R2) / R1
actual_voltage = voltage * DIV_RATIO # voltage division compensation
percent = min(max((actual_voltage - 3.3) / (Vref_BAT - 3.3) * 100, 0), 100)
return percent, actual_voltage
def draw_battery(percent):
oled.fill(0)
oled.text('{:.0f}%'.format(percent), 0, 17)
# draw battery cartoon icon
oled.rect(0, 0, 30, 15, 1) # frame (x,y,width,height)
oled.rect(30, 5, 3, 5, 1) # anode
oled.fill_rect(2, 2, int(26 * percent / 100), 11, 1) # electric percent column
oled.rotate(0)
oled.show()
def BAT_display(percent,x,y): # battery percent, icon position (x,y)
oled.fill(0)
oled.text('{:.0f}%'.format(percent), 0+x, 17+y)
# draw battery cartoon icon
oled.rect(0+x, 0+y, 30, 15, 1) # frame (x,y,width,height)
oled.rect(30+x, 5+y, 3, 5, 1) # anode
oled.fill_rect(2+x, 2+y, int(26 * percent / 100), 11, 1) # electric percent column
oled.rotate(0)
oled.show()
def draw_vertical_battery(percent,x,y): # battery percent, icon position (x,y)
oled.fill(0)
oled.text('{:.0f}'.format(percent), 0+x, 33+y)
# draw battery cartoon icon
oled.rect(0+x, 2+y, 15, 30, 1) # frame (x,y,width,height)
oled.rect(5+x, 0+y, 5, 3, 1) # anode
fill_h = int(27 * percent / 100)
oled.fill_rect(2+x, 2 + (28 - fill_h) + y, 11, fill_h, 1) # percent column
oled.rotate(0)
oled.show()
while True:
percent, voltage = get_battery_level()
#draw_battery(percent)
BAT_display(percent,90,2)
#draw_vertical_battery(percent,90,9)
print('Battery Voltage: {:.2f} V, Battery Level: {:.1f}%'.format(voltage,percent))
utime.sleep(2)
保存代碼,連接開發(fā)板,配置解釋器并運(yùn)行。
效果
電量圖標(biāo)的水平顯示
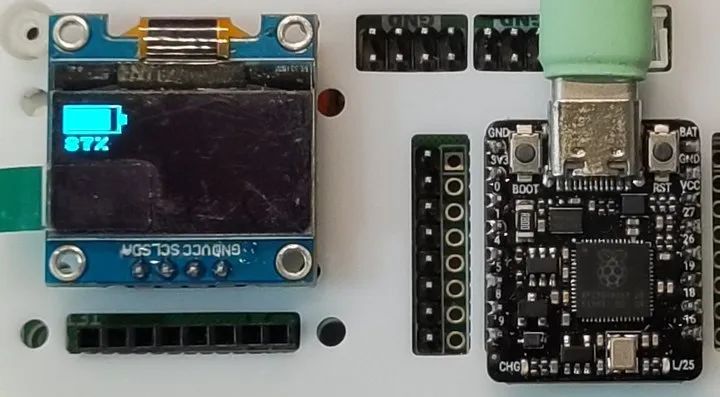
電量圖標(biāo)的豎直顯示
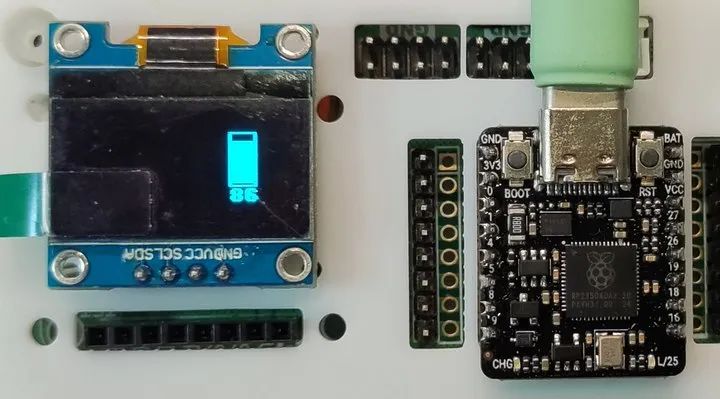
3. DHT11 溫濕度計(jì)
帶電量顯示的 DHT11 溫濕度計(jì)
代碼
from machine import Pin, ADC, I2C
from PicoDHT22 import PicoDHT22
import ssd1306
import utime
# initialize ADC pin
adc = ADC(Pin(29))
# initialize OLED
i2c = I2C(0, scl=Pin(5), sda=Pin(4))
oled = ssd1306.SSD1306_I2C(128, 64, i2c)
# parameters of voltage divide resistor
R1, R2 = 1000000, 1000000
Vref_BAT = 3.81 # battery voltage in full charged state
def get_battery_level():
adc_value = adc.read_u16()
voltage = (adc_value / 65535) * 3.3
DIV_RATIO = (R1 + R2) / R1
actual_voltage = voltage * DIV_RATIO # voltage division compensation
percent = min(max((actual_voltage - 3.3) / (Vref_BAT - 3.3) * 100, 0), 100)
return percent, actual_voltage
def draw_battery(percent):
oled.fill(0)
oled.text('{:.0f}%'.format(percent), 90, 27)
# draw battery cartoon icon
oled.rect(90, 10, 30, 15, 1) # frame
oled.rect(120, 15, 3, 5, 1) # anode
oled.fill_rect(92, 12, int(26 * percent / 100), 11, 1) # electric percent column
oled.show()
def BAT_display(percent):
oled.fill(0)
oled.text('{:.0f}%'.format(percent), 90, 27)
# draw battery cartoon icon
oled.rect(90, 10, 30, 15, 1) # frame
oled.rect(120, 15, 3, 5, 1) # anode
oled.fill_rect(92, 12, int(26 * percent / 100), 11, 1)
oled.show()
def draw_vertical_battery(percent,x,y):
# 局部清屏并顯示電量百分比
oled.fill_rect(x,y,15+8,30+16,0)
oled.text('{:.0f}'.format(percent), 0+x, 33+y)
# 豎版電池繪制
oled.rect(0+x, 2+y, 15, 30, 1) # frame (x,y,width,height)
oled.rect(5+x, 0+y, 5, 3, 1) # anode
fill_h = int(26 * percent / 100)
oled.fill_rect(2+x, 2 + (28 - fill_h) + y, 11, fill_h, 1) # percent column
oled.rotate(0)
oled.show()
def display_TH(temp,humi):
oled.fill_rect(20,15,6*8,64-15,0) # 局部清屏
oled.text("Temperature:", 0, 0)
oled.text("{:.1f} C".format(temp), 20, 15)
oled.text("Humidity:", 0, 35)
oled.text("{:.1f} %".format(humi), 20, 50)
oled.rotate(0) # rotate the screen display for a more comfortable position
oled.show()
dht_sensor=PicoDHT22(Pin(0,Pin.IN,Pin.PULL_UP),dht11=True)
while True:
temp,humi = dht_sensor.read()
percent, voltage = get_battery_level()
#draw_battery(percent)
#BAT_display(percent)
draw_vertical_battery(percent,90,16)
display_TH(temp,humi)
print('Battery Voltage: {:.2f} V, Battery Level: {:.1f}%'.format(voltage,percent))
utime.sleep(2)
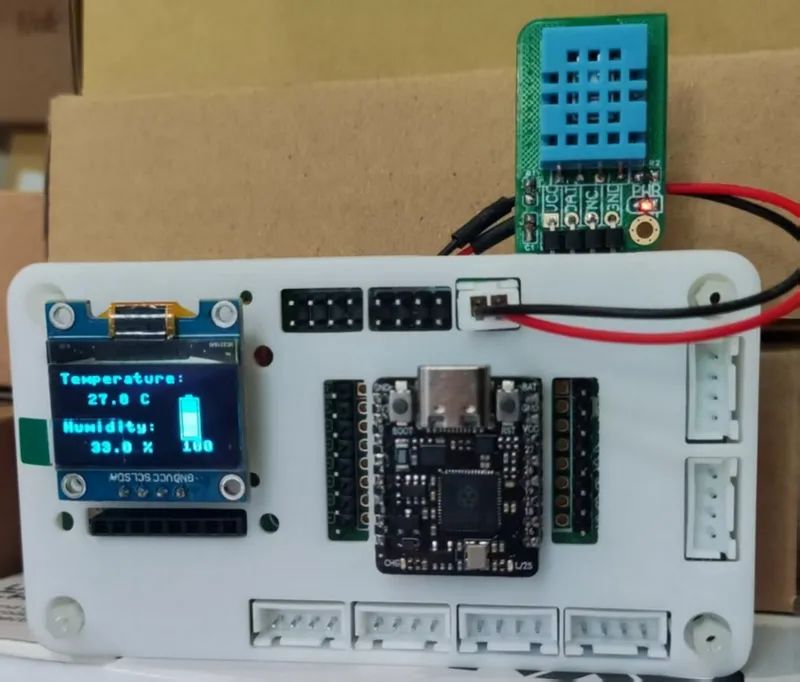
效果
電量和溫濕度顯示,數(shù)據(jù)刷新的時(shí)間間隔為 2 秒

4. 眨眼動(dòng)畫
OLED 顯示矩形填充狀眼睛,改變形狀并利用人眼的視覺暫留效應(yīng)實(shí)現(xiàn)眨眼效果。
代碼
from machine import Pin, I2C
import ssd1306
import utime
import urandom
i2c = I2C(0, scl=Pin(5), sda=Pin(4))
oled_width = 128
oled_height = 64
oled = ssd1306.SSD1306_I2C(oled_width, oled_height, i2c)
def draw_eyes(state,xshift,yshift):
"""state: 0=完全睜開, 1=半閉, 2=完全閉上"""
width,height = (int)(oled_width/5),(int)(oled_height/3)
cx,cy = (int)((oled_width-2.5*width)/2),(int)((oled_height-height)/2) # eyes at scrren center 定位點(diǎn)為矩形左上角
x = cx + xshift
y = cy + yshift
oled.fill_rect(x, y, int(2.5*width), height, 0)
# draw left eye
if state == 0: # 完全睜開
oled.fill_rect(x, y, width, height, 1)
elif state == 1: # 半閉
oled.fill_rect(x, y+(int)(height/4), width, (int)(height/2), 1)
else: # 完全閉上
oled.hline(x, y+(int)(height/2), width, 1)
# draw right eye
if state == 0: # 完全睜開
oled.fill_rect(x+width+(int)(width/2), y, width, height, 1)
elif state == 1: # 半閉
oled.fill_rect(x+width+(int)(width/2), y+(int)(height/4), width, (int)(height/2), 1)
else: # 完全閉上
oled.hline(x+width+(int)(width/2), y+(int)(height/2), width, 1)
oled.show()
def blink_eyes(xshift,yshift):
# 睜眼狀態(tài)保持
draw_eyes(0,xshift,yshift)
utime.sleep(1)
# 眨眼動(dòng)畫序列
draw_eyes(1,xshift,yshift) # 半閉
utime.sleep(0.1)
draw_eyes(2,xshift,yshift) # 全閉
utime.sleep(0.1)
draw_eyes(1,xshift,yshift) # 半閉
utime.sleep(0.1)
draw_eyes(0,xshift,yshift) # 全開
def random_eyes():
xshift = urandom.randint(-(int)(oled_width/4),(int)(oled_width/4))
yshift = urandom.randint(-(int)(oled_height/3),(int)(oled_height/3))
oled.fill(0)
blink_eyes(xshift,yshift)
#print(xshift,yshift)
while True:
random_eyes()
#blink_eyes(0,0)
保存代碼,連接開發(fā)板,配置解釋器并運(yùn)行。
效果
眨眼效果(眼睛位置在屏幕內(nèi)隨機(jī)移動(dòng))

四、工程代碼
將工程調(diào)試的代碼合并,實(shí)現(xiàn)溫濕度數(shù)據(jù)(包括電池電量)與息屏隨機(jī)眨眼動(dòng)畫的切換顯示。
from machine import Pin, ADC, I2C
from PicoDHT22 import PicoDHT22
import ssd1306
import utime
import urandom
# initialize ADC pin
adc = ADC(Pin(29))
# initialize OLED
i2c = I2C(0, scl=Pin(5), sda=Pin(4))
oled_width = 128
oled_height = 64
oled = ssd1306.SSD1306_I2C(oled_width, oled_height, i2c)
# parameters of voltage divide resistor
R1, R2 = 1000000, 1000000
Vref_BAT = 3.81 # battery voltage in full charged state
def get_battery_level():
adc_value = adc.read_u16()
voltage = (adc_value / 65535) * 3.3
DIV_RATIO = (R1 + R2) / R1
actual_voltage = voltage * DIV_RATIO # voltage division compensation
percent = min(max((actual_voltage - 3.3) / (Vref_BAT - 3.3) * 100, 0), 100)
return percent, actual_voltage
def draw_vertical_battery(percent,x,y):
# 局部清屏并顯示電量百分比
oled.fill_rect(x,y,15+8,30+16,0)
oled.text('{:.0f}'.format(percent), 0+x, 33+y)
# 豎版電池繪制
oled.rect(0+x, 2+y, 15, 30, 1) # frame (x,y,width,height)
oled.rect(5+x, 0+y, 5, 3, 1) # anode
fill_h = int(26 * percent / 100)
oled.fill_rect(2+x, 2 + (28 - fill_h) + y, 11, fill_h, 1) # percent column
oled.rotate(0)
oled.show()
def display_TH(temp,humi):
oled.fill_rect(20,15,6*8,64-15,0) # part clear
oled.text("Temperature:", 0, 0)
oled.text("{:.1f} C".format(temp), 20, 15)
oled.text("Humidity:", 0, 35)
oled.text("{:.1f} %".format(humi), 20, 50)
oled.rotate(0) # rotate the screen display for a more comfortable position
oled.show()
def draw_eyes(state,xshift,yshift):
"""state: 0=full open, 1=half open, 2=close"""
width,height = (int)(oled_width/5),(int)(oled_height/3)
cx,cy = (int)((oled_width-2.5*width)/2),(int)((oled_height-height)/2) # eyes at scrren center
x = cx + xshift
y = cy + yshift
oled.fill_rect(x, y, int(2.5*width), height, 0)
# draw left eye
if state == 0: # full open
oled.fill_rect(x, y, width, height, 1)
elif state == 1: # half open
oled.fill_rect(x, y+(int)(height/4), width, (int)(height/2), 1)
else: # close
oled.hline(x, y+(int)(height/2), width, 1)
# draw right eye
if state == 0: # full open
oled.fill_rect(x+width+(int)(width/2), y, width, height, 1)
elif state == 1: # half open
oled.fill_rect(x+width+(int)(width/2), y+(int)(height/4), width, (int)(height/2), 1)
else: # close
oled.hline(x+width+(int)(width/2), y+(int)(height/2), width, 1)
oled.show()
def blink_eyes(xshift,yshift):
# keep opening
draw_eyes(0,xshift,yshift)
utime.sleep(0.5)
# blink eyes order
draw_eyes(1,xshift,yshift) # half open
utime.sleep(0.1)
draw_eyes(2,xshift,yshift) # close
utime.sleep(0.1)
draw_eyes(1,xshift,yshift) # half open
utime.sleep(0.1)
draw_eyes(0,xshift,yshift) # full open
utime.sleep(0.5)
def random_eyes():
xshift = urandom.randint(-(int)(oled_width/4),(int)(oled_width/4))
yshift = urandom.randint(-(int)(oled_height/3),(int)(oled_height/3))
oled.fill(0)
blink_eyes(xshift,yshift)
#print(xshift,yshift)
dht_sensor = PicoDHT22(Pin(0,Pin.IN,Pin.PULL_UP),dht11=True)
def TH_BAT():
''' temperature and humidity and battery '''
temp,humi = dht_sensor.read()
percent, voltage = get_battery_level()
oled.fill(0)
display_TH(temp,humi)
draw_vertical_battery(percent,90,16)
print('Temperature: {:.2f} C, Humidity: {:.2f} RH, Battery Voltage: {:.2f} V, Battery Level: {:.1f}%'.format(temp,humi,voltage,percent))
utime.sleep(2)
while True:
TH_BAT()
random_eyes()
連接開發(fā)板,配置解釋器,將代碼保存至根目錄,取下數(shù)據(jù)線,連接電池,實(shí)現(xiàn)顯示效果。
五、最終效果展示
幀動(dòng)畫分別如下
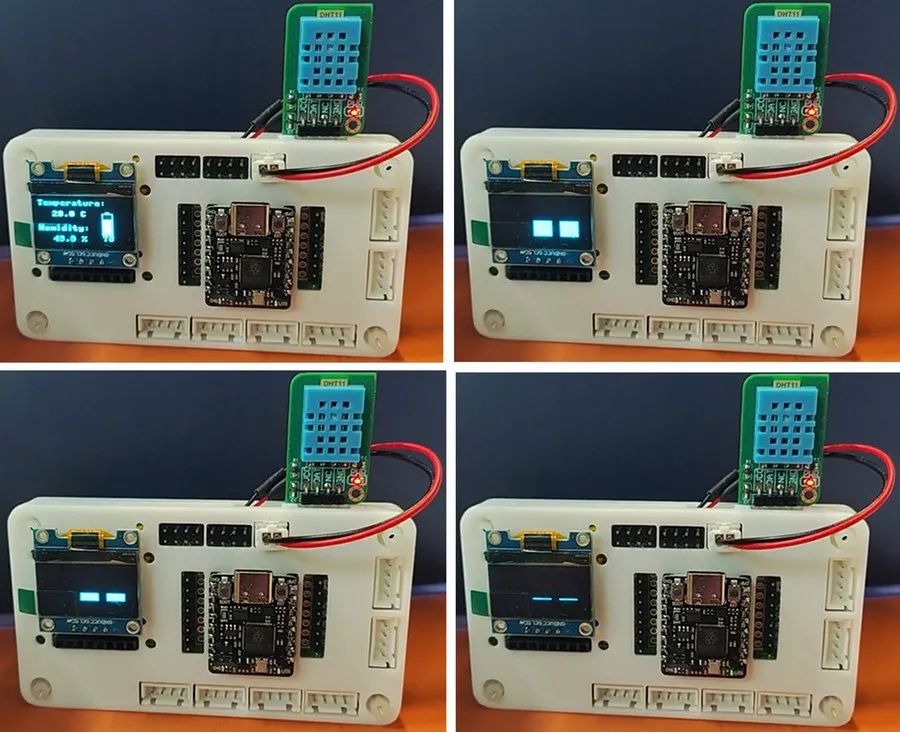
六、項(xiàng)目總結(jié)
本文介紹了樹莓派 RP2350 開發(fā)板結(jié)合 DHT11 模塊、鋰電池模塊、隨機(jī)眨眼動(dòng)畫,實(shí)現(xiàn) OLED 顯示的桌面動(dòng)態(tài)溫濕度計(jì)的項(xiàng)目設(shè)計(jì)。通過多任務(wù)結(jié)合,為更多 DIY 設(shè)計(jì)提供了可能,如添加按鍵掃描或語音控制模塊,實(shí)現(xiàn)指定的功能切換與人機(jī)交互,拓展和豐富了該開發(fā)板在物聯(lián)網(wǎng)領(lǐng)域的創(chuàng)新與應(yīng)用,為 RP2350 的開發(fā)設(shè)計(jì)和產(chǎn)品應(yīng)用提供了參考。
-
DIY
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
176文章
894瀏覽量
353144 -
溫濕度計(jì)
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
1文章
26瀏覽量
8524 -
樹莓派
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
121文章
2001瀏覽量
107429
發(fā)布評(píng)論請(qǐng)先 登錄
基于CW32L083設(shè)計(jì)的超低功耗溫濕度計(jì)

樹莓派Pico 2發(fā)布,搭載RP2350雙核RISC-V和Arm Cortex-M33微控制器!
樹莓派RP2350 - 桌面動(dòng)態(tài)溫濕度計(jì)
DHT11溫濕度計(jì) 實(shí)時(shí)溫濕度記錄曲線 記錄存盤 上下限報(bào)警 .....
藍(lán)牙溫濕度計(jì)常用的場(chǎng)景
【天啟教育M1開發(fā)板試用體驗(yàn)】MQTT溫濕度計(jì)
如何自己設(shè)計(jì)一款溫濕度計(jì)

溫濕度計(jì)怎么使用_溫濕度計(jì)怎么調(diào)
工業(yè)級(jí)溫濕度傳感器與日常溫濕度計(jì)的區(qū)別
溫濕度計(jì)(物聯(lián)網(wǎng))開源

RP2350 現(xiàn)已上市!變體即將發(fā)布!






 用樹莓派RP2350 DIY 桌面動(dòng)態(tài)溫濕度計(jì)
用樹莓派RP2350 DIY 桌面動(dòng)態(tài)溫濕度計(jì)












評(píng)論