使用 Musl C 庫的時候,內(nèi)核提供了基于 LOS_XXX 適配實現(xiàn) pthread、mqeue、fs、semaphore、time 等模塊的 posix 接口(//kernel/liteos_m/kal/posix)。內(nèi)核提供的 posix 接口與 musl 中的標準 C 庫接口共同組成 LiteOS-M 的 LibC。編譯時使用 arm-none-eabi-gcc,但只使用其工具鏈的編譯功能,通過加上 - nostdinc 與 - nostdlib 強制使用我們自己改造后的 musl-C。
社區(qū)及三方廠商開發(fā)多使用公版工具鏈 arm-none-eabi-gcc 加上私有定制優(yōu)化進行編譯,LiteOS-M 內(nèi)核也支持公版 arm-none-eabi-gcc C 庫編譯內(nèi)核運行。newlib 是小型 C 庫,針對 posix 接口涉及系統(tǒng)調(diào)用的部分,newlib 提供一些需要系統(tǒng)適配的鉤子函數(shù),例如_exit (),_open (),_close (),_gettimeofday () 等,操作系統(tǒng)適配這些鉤子,就可以使用公版 newlib 工具鏈編譯運行程序。
1、Newlib C 文件系統(tǒng)
在使用 Newlib C 并且使能支持 POSIX FS API 時(可以在 kernelliteos-m 目錄下,執(zhí)行 make meuconfig 彈出配置界面,路徑為 Compat-Choose libc implementation),如下圖所示。可以使用文件 kallibcnewlibportingsrcfs.c 中定義的文件系統(tǒng)操作接口。這些是標準的 POSIX 接口,如果想了解 POSIX 用法,可以在 linux 平臺輸入 man -a 函數(shù)名稱,比如 man -a opendir 來打開函數(shù)的手冊。
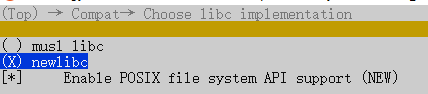
1.1 函數(shù) mount、umount 和 umount2
這些函數(shù)的用法,函數(shù)實現(xiàn)和 musl c 部分一致。
int mount(const char *source, const char *target,
const char *filesystemtype, unsigned long mountflags,
const void *data)
{
return LOS_FsMount(source, target, filesystemtype, mountflags, data);
}
int umount(const char *target)
{
return LOS_FsUmount(target);
}
int umount2(const char *target, int flag)
{
return LOS_FsUmount2(target, flag);
}
1.2 文件操作接口
以下劃線開頭的函數(shù)實現(xiàn)是 newlib c 的鉤子函數(shù)實現(xiàn)。有關(guān) newlib 的鉤子函數(shù)調(diào)用過程下文專門分析下。
int _open(const char *path, int oflag, ...)
{
va_list vaList;
va_start(vaList, oflag);
int ret;
ret = LOS_Open(path, oflag);
va_end(vaList);
return ret;
}
int _close(int fd)
{
return LOS_Close(fd);
}
ssize_t _read(int fd, void *buf, size_t nbyte)
{
return LOS_Read(fd, buf, nbyte);
}
ssize_t _write(int fd, const void *buf, size_t nbyte)
{
return LOS_Write(fd, buf, nbyte);
}
off_t _lseek(int fd, off_t offset, int whence)
{
return LOS_Lseek(fd, offset, whence);
}
int _unlink(const char *path)
{
return LOS_Unlink(path);
}
int _fstat(int fd, struct stat *buf)
{
return LOS_Fstat(fd, buf);
}
int _stat(const char *path, struct stat *buf)
{
return LOS_Stat(path, buf);
}
int fsync(int fd)
{
return LOS_Fsync(fd);
}
int mkdir(const char *path, mode_t mode)
{
return LOS_Mkdir(path, mode);
}
DIR *opendir(const char *dirName)
{
return LOS_Opendir(dirName);
}
struct dirent *readdir(DIR *dir)
{
return LOS_Readdir(dir);
}
int closedir(DIR *dir)
{
return LOS_Closedir(dir);
}
int rmdir(const char *path)
{
return LOS_Unlink(path);
}
int rename(const char *oldName, const char *newName)
{
return LOS_Rename(oldName, newName);
}
int statfs(const char *path, struct statfs *buf)
{
return LOS_Statfs(path, buf);
}
int ftruncate(int fd, off_t length)
{
return LOS_Ftruncate(fd, length);
}
在 newlib 沒有使能使能支持 POSIX FS API 時時,需要提供這些鉤子函數(shù)的空的實現(xiàn),返回 - 1 錯誤碼即可。
int _open(const char *path, int oflag, ...)
{
return -1;
}
int _close(int fd)
{
return -1;
}
ssize_t _read(int fd, void *buf, size_t nbyte)
{
return -1;
}
ssize_t _write(int fd, const void *buf, size_t nbyte)
{
return -1;
}
off_t _lseek(int fd, off_t offset, int whence)
{
return -1;
}
int _unlink(const char *path)
{
return -1;
}
int _fstat(int fd, struct stat *buf)
{
return -1;
}
int _stat(const char *path, struct stat *buf)
{
return -1;
}
2、Newlib C 內(nèi)存分配釋放
實現(xiàn) malloc 適配有以下兩種方法:
實現(xiàn) _sbrk_r 函數(shù)。這種方法中,內(nèi)存分配函數(shù)使用 newlib 中的。
實現(xiàn) _malloc_r, _realloc_r, _free_r, _memalign_r, _malloc_usable_size_r 等。這種方法中,內(nèi)存分配函數(shù)可以使用內(nèi)核的。
為了方便地根據(jù)業(yè)務(wù)進行內(nèi)存分配算法調(diào)優(yōu)和問題定位,推薦選擇后者。內(nèi)核的內(nèi)存函數(shù)定義在文件 kallibcnewlibportingsrcmalloc.c 中。源碼片段如下,代碼實現(xiàn)比較簡單,不再分析源碼。
......
void __wrap__free_r(struct _reent *reent, void *aptr)
{
if (aptr == NULL) {
return;
}
LOS_MemFree(OS_SYS_MEM_ADDR, aptr);
}
size_t __wrap__malloc_usable_size_r(struct _reent *reent, void *aptr)
{
return 0;
}
void *__wrap__malloc_r(struct _reent *reent, size_t nbytes)
{
if (nbytes == 0) {
return NULL;
}
return LOS_MemAlloc(OS_SYS_MEM_ADDR, nbytes);
}
void *__wrap__memalign_r(struct _reent *reent, size_t align, size_t nbytes)
{
if (nbytes == 0) {
return NULL;
}
return LOS_MemAllocAlign(OS_SYS_MEM_ADDR, nbytes, align);
}
......
可能已經(jīng)注意到函數(shù)命名由__wrap_加上鉤子函數(shù)名稱兩部分組成。這是因為 newlib 中已經(jīng)存在這些函數(shù)的符號,因此需要用到 gcc 的 wrap 的鏈接選項替換這些函數(shù)符號為內(nèi)核的實現(xiàn),在設(shè)備開發(fā)板的配置文件中,比如 //device/board/fnlink/v200zr/liteos_m/config.gni,新增這些函數(shù)的 wrap 鏈接選項,示例如下:
board_ld_flags += [
"-Wl,--wrap=_malloc_r",
"-Wl,--wrap=_realloc_r",
"-Wl,--wrap=_free_r",
"-Wl,--wrap=_memalign_r",
"-Wl,--wrap=_malloc_usable_size_r",
]
3、Newlib 鉤子函數(shù)介紹
以 open 函數(shù)的鉤子函數(shù)_open 為例來介紹 newlib 的鉤子函數(shù)的調(diào)用過程。open () 函數(shù)實現(xiàn)在 newlib-cygwinnewliblibcsyscallssysopen.c 中,該函數(shù)會進一步調(diào)用函數(shù)_open_r,這是個可重入函數(shù) Reentrant Function,支持在多線程中運行。
int
open (const char *file,
int flags, ...)
{
va_list ap;
int ret;
va_start (ap, flags);
ret = _open_r (_REENT, file, flags, va_arg (ap, int));
va_end (ap);
return ret;
}
所有的可重入函數(shù)定義在文件夾 newlib-cygwinnewliblibcreent,函數(shù)_open_r 定義在該文件夾的文件 newlib-cygwinnewliblibcreentopenr.c 里。函數(shù)代碼如下:
int
_open_r (struct _reent *ptr,
const char *file,
int flags,
int mode)
{
int ret;
errno = 0;
if ((ret = _open (file, flags, mode)) == -1 && errno != 0)
ptr->_errno = errno;
return ret;
}
函數(shù)_open_r 如上述代碼所示,會進一步調(diào)用函數(shù)_open,該函數(shù),以 arm 硬件平臺為例,實現(xiàn)在 newlib-cygwinlibglossarmsyscalls.c 文件里。newlib 目錄是和硬件平臺無關(guān)的痛毆他那個功能實現(xiàn),libloss 目錄是底層的驅(qū)動實現(xiàn),以各個硬件平臺為文件夾進行組織。在特定硬件平臺的目錄下的 syscalls.c 文件里面實現(xiàn)了 newlib 需要的各個樁函數(shù):
/* Forward prototypes. */ int _system (const char *); int _rename (const char *, const char *); int _isatty (int); clock_t _times (struct tms *); int _gettimeofday (struct timeval *, void *); int _unlink (const char *); int _link (const char *, const char *); int _stat (const char *, struct stat *); int _fstat (int, struct stat *); int _swistat (int fd, struct stat * st); void * _sbrk (ptrdiff_t); pid_t _getpid (void); int _close (int); clock_t _clock (void); int _swiclose (int); int _open (const char *, int, ...); int _swiopen (const char *, int); int _write (int, const void *, size_t); int _swiwrite (int, const void *, size_t); _off_t _lseek (int, _off_t, int); _off_t _swilseek (int, _off_t, int); int _read (int, void *, size_t); int _swiread (int, void *, size_t); void initialise_monitor_handles (void);
對于上文提到的函數(shù)_open,源碼如下。后續(xù)不再繼續(xù)分析了,LiteOS-M 內(nèi)核會提供這些鉤子函數(shù)的實現(xiàn)。
int
_open (const char * path, int flags, ...)
{
return _swiopen (path, flags);
}
審核編輯 黃宇
-
內(nèi)核
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
3文章
1410瀏覽量
41112 -
源碼
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
8文章
668瀏覽量
30148 -
Posix
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
0文章
36瀏覽量
9780 -
鴻蒙
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
59文章
2526瀏覽量
43782
發(fā)布評論請先 登錄
鴻蒙內(nèi)核源碼Task/線程技術(shù)分析
鴻蒙內(nèi)核源碼分析:用通俗易懂的語言告訴你鴻蒙內(nèi)核發(fā)生了什么?
鴻蒙內(nèi)核源碼分析(源碼注釋篇):給HarmonyOS源碼逐行加上中文注釋
鴻蒙內(nèi)核源碼分析:給HarmonyOS源碼逐行加上中文注釋
鴻蒙內(nèi)核源碼分析(必讀篇):用故事說內(nèi)核
鴻蒙內(nèi)核源碼分析(雙循環(huán)鏈表篇) :內(nèi)核最重要結(jié)構(gòu)體
鴻蒙內(nèi)核源碼分析(必讀篇)
HarmonyOS內(nèi)核源碼分析(上)電子書-上線了
鴻蒙內(nèi)核源碼分析(百篇博客分析.挖透鴻蒙內(nèi)核)
為何要精讀鴻蒙內(nèi)核源碼?

鴻蒙內(nèi)核源碼分析:鴻蒙內(nèi)核的每段匯編代碼解析
鴻蒙內(nèi)核源碼分析: 虛擬內(nèi)存和物理內(nèi)存是怎么管理的

鴻蒙內(nèi)核源碼分析 :內(nèi)核最重要結(jié)構(gòu)體





 鴻蒙輕內(nèi)核源碼分析:Newlib C
鴻蒙輕內(nèi)核源碼分析:Newlib C










評論