1 ResultSet(結(jié)果集)
ResultSet(結(jié)果集)是OpenHarmony關系型數(shù)據(jù)庫提供查詢數(shù)據(jù)表返回結(jié)果的方法,提供了多種靈活的數(shù)據(jù)訪問方式,以便于開發(fā)者獲取各項數(shù)據(jù),ResultSet屬性如表1-1所示,ResultSet方法如表1-2所示。
表1-1 ResultSet屬性
| 名稱 | 類型 | 必填 | 說明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| columnNames | Array | 是 | 結(jié)果集中所有列的名稱 |
| columnCount | number | 是 | 結(jié)果集中的列數(shù) |
| rowCount | number | 是 | 結(jié)果集中的行數(shù) |
| rowIndex | number | 是 | 結(jié)果集當前行的索引 |
| isAtFirstRow | boolean | 是 | 結(jié)果集是否位于第一行 |
| isAtLastRow | boolean | 是 | 結(jié)果集是否位于最后一行 |
| isEnded | boolean | 是 | 結(jié)果集是否位于最后一行之后 |
| isStarted | boolean | 是 | 指針是否移動過 |
| isClosed | boolean | 是 | 當前結(jié)果集是否關閉 |
表1-2 ResultSet方法
| 名稱 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| getColumnIndex(columnName: string): number | 根據(jù)指定的列名獲取列索引columnName: 結(jié)果集中指定列的名稱 number: 返回指定列的索引 |
| getColumnName(columnIndex: number): string | 根據(jù)指定的列索引獲取列名columnIndex: 結(jié)果集中指定列的索引string: 返回指定列的名稱 |
| goTo(offset: number): boolean | 向前或向后轉(zhuǎn)至結(jié)果集的指定行,相對于當前行位置偏移offset: 表示相對于當前行位置偏移量boolean:操作成功,則為true,否則為false |
| goToRow(position: number): boolean | 轉(zhuǎn)到結(jié)果集的指定行position: 表示要移動到的指定位置boolean: 操作成功,則為true,否則為false |
| goToFirstRow(): boolean | 轉(zhuǎn)到結(jié)果集的第一行boolean: 操作成功,則為true,否則為false |
| goToLastRow(): boolean | 轉(zhuǎn)到結(jié)果集的最后一行boolean: 操作成功,則為true,否則為false |
| goToNextRow(): boolean | 轉(zhuǎn)到結(jié)果集的下一行boolean: 操作成功,則為true,否則為false |
| goToPreviousRow(): boolean | 轉(zhuǎn)到結(jié)果集上一行boolean: 操作成功,則為true,否則為false |
| getBlob(columnIndex: number): Uint8Array | 以字節(jié)數(shù)組的形式獲取當前行中指定列的值指定的列索引,從0開始Uint8Array: 以字節(jié)數(shù)組的形式返回指定列的值 |
| getString(columnIndex: number): string | 以字符串形式獲取當前行中指定列的值columnIndex: 指定的列索引,從0開始string: 以字符串形式返回指定列的值 |
| getLong(columnIndex: number): number | 以Long形式獲取當前行中指定列的值columnIndex: 指定的列索引,從0開始number: 以Long形式返回指定列的值。該接口支持的數(shù)據(jù)范圍是:Number.MIN_SAFE_INTEGER~Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER,若超出該范圍,則建議使用getDouble |
| getDouble(columnIndex: number): number | 以double形式獲取當前行中指定列的值columnIndex: 指定的列索引,從0開始number: 以double形式返回指定列的值 |
| isColumnNull(columnIndex: number): boolean | 檢查當前行中指定列的值是否為nullcolumnIndex: 指定的列索引,從0開始boolean: 當前行中指定列的值為null,則返回true,否則為false |
| close(): void | 關閉結(jié)果集 |
2 流程
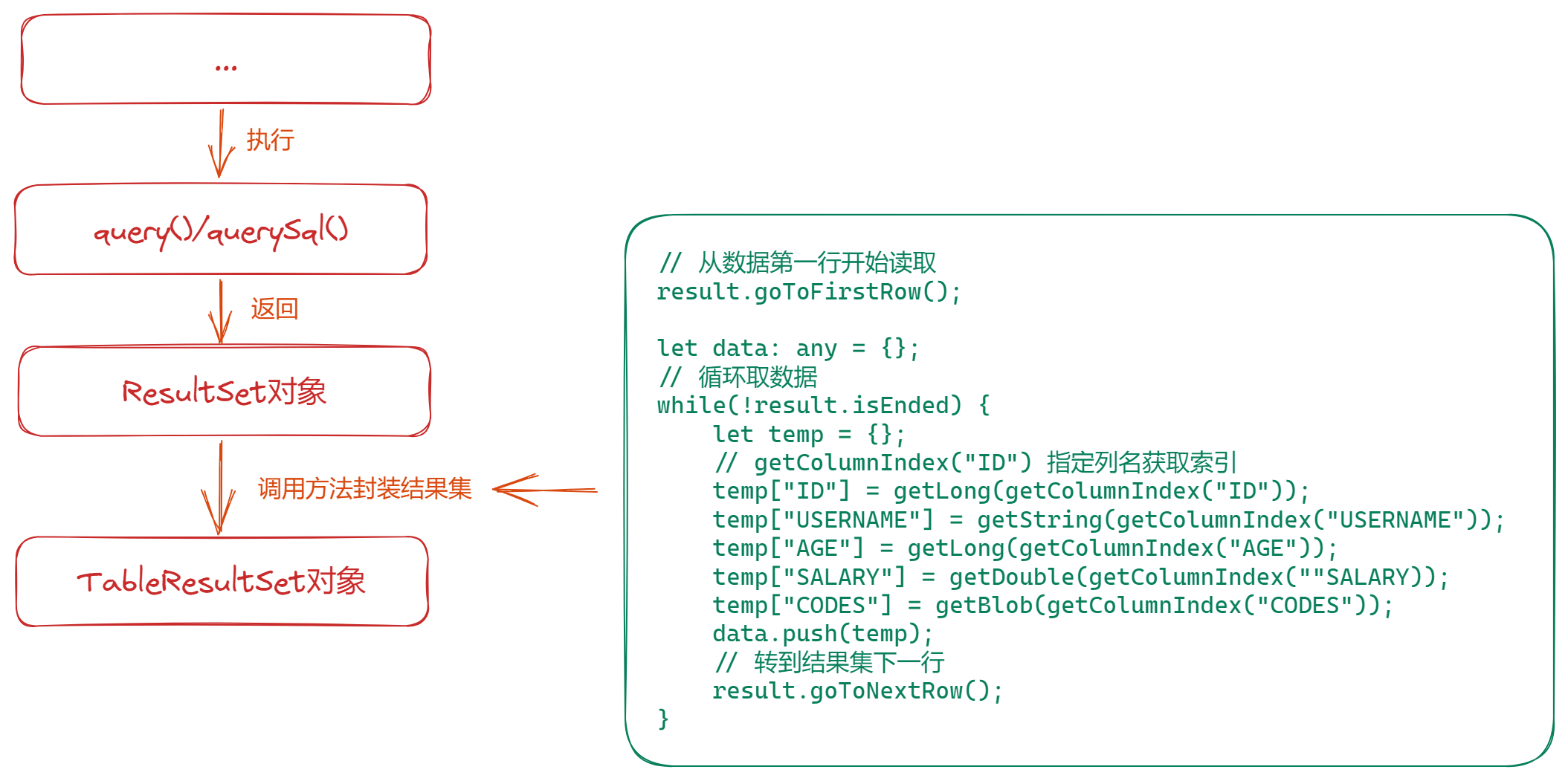
3 步驟
3.1 獲取ResultSet結(jié)果集
通過RdbStore實例的query()或querySql()方法獲得ResultSet結(jié)果集。
let predicates = new relationalStore.RdbPredicates(this.tableName);
let result = await this.rdbStore.query(predicates, columns);
3.2 自定義返回結(jié)果類
自定義TableResultSet類用于前臺展示。
export class TableResultSet {
private total: number; // 總條數(shù)
private data: any; // 數(shù)據(jù)表數(shù)據(jù)
setTotal(total: number) {
this.total = total;
}
setData(data: any) {
this.data = data;
}
}
3.3 結(jié)果集轉(zhuǎn)返回結(jié)果
ResultSet并不能直接用來展示,通過ResultSet提供的各類方法獲取需要的信息。
private resultToObject(result: relationalStore.ResultSet) {
let trs = new TableResultSet();
trs.setData(result.rowCount);
let data: Array<any> = [];
let count = result.rowCount;
if (count === 0 || typeof count === 'string') {
trs.setData([]);
} else {
// 從數(shù)據(jù)第一行開始讀取
result.goToFirstRow();
for (let j = 0; j < count; j++) {
let temp: any = {};
for (let i = 0; i < this.fields.length; i++) {
let field = this.fields[i];
if (field.type === 'INTEGER' || field.type === 'integer') {
temp[field.name] = result.getLong(result.getColumnIndex(field.name));
} else if (field.type === 'REAL' || field.type === 'real') {
temp[field.name] = result.getDouble(result.getColumnIndex(field.name));
} else if (field.type === 'TEXT' || field.type === 'text') {
temp[field.name] = result.getString(result.getColumnIndex(field.name));
} else if (field.type === 'BLOB' || field.type === 'blob') {
temp[field.name] = result.getBlob(result.getColumnIndex(field.name));
}
}
data.push(temp);
result.goToNextRow();
}
trs.setData(data);
}
return trs;
}
4 呈現(xiàn)結(jié)果
- 使用斷點調(diào)試方式
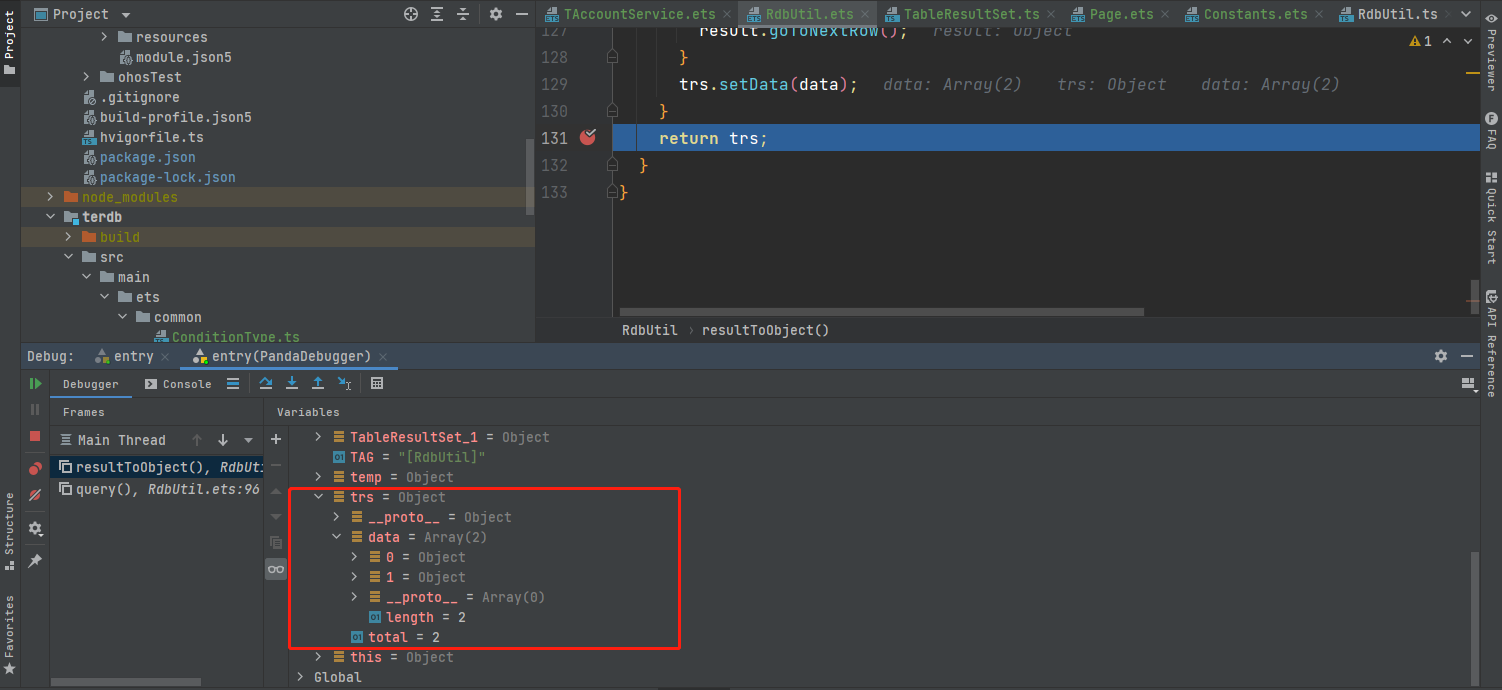
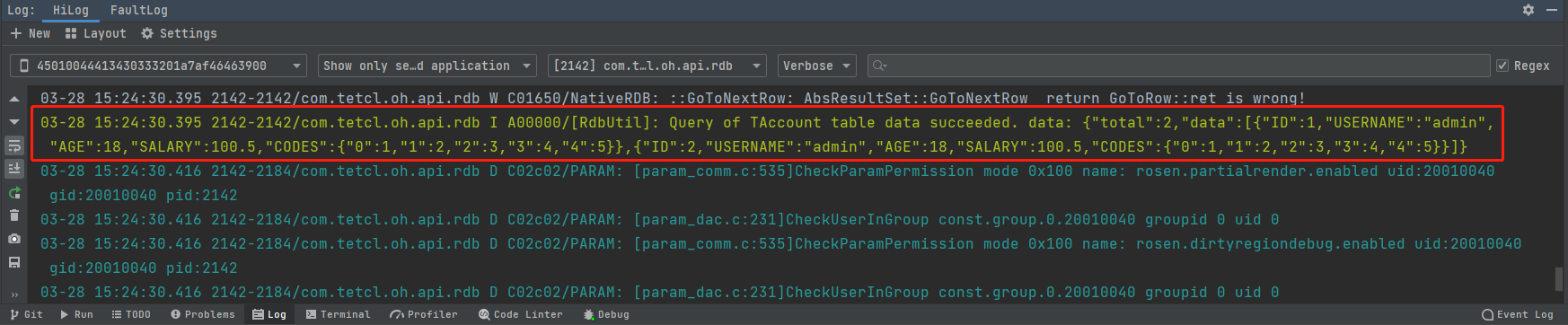
- 使用日志調(diào)試方式
Log.info(TAG, `Query of ${this.tableName} table data succeeded. data: ` + JSON.stringify(result));
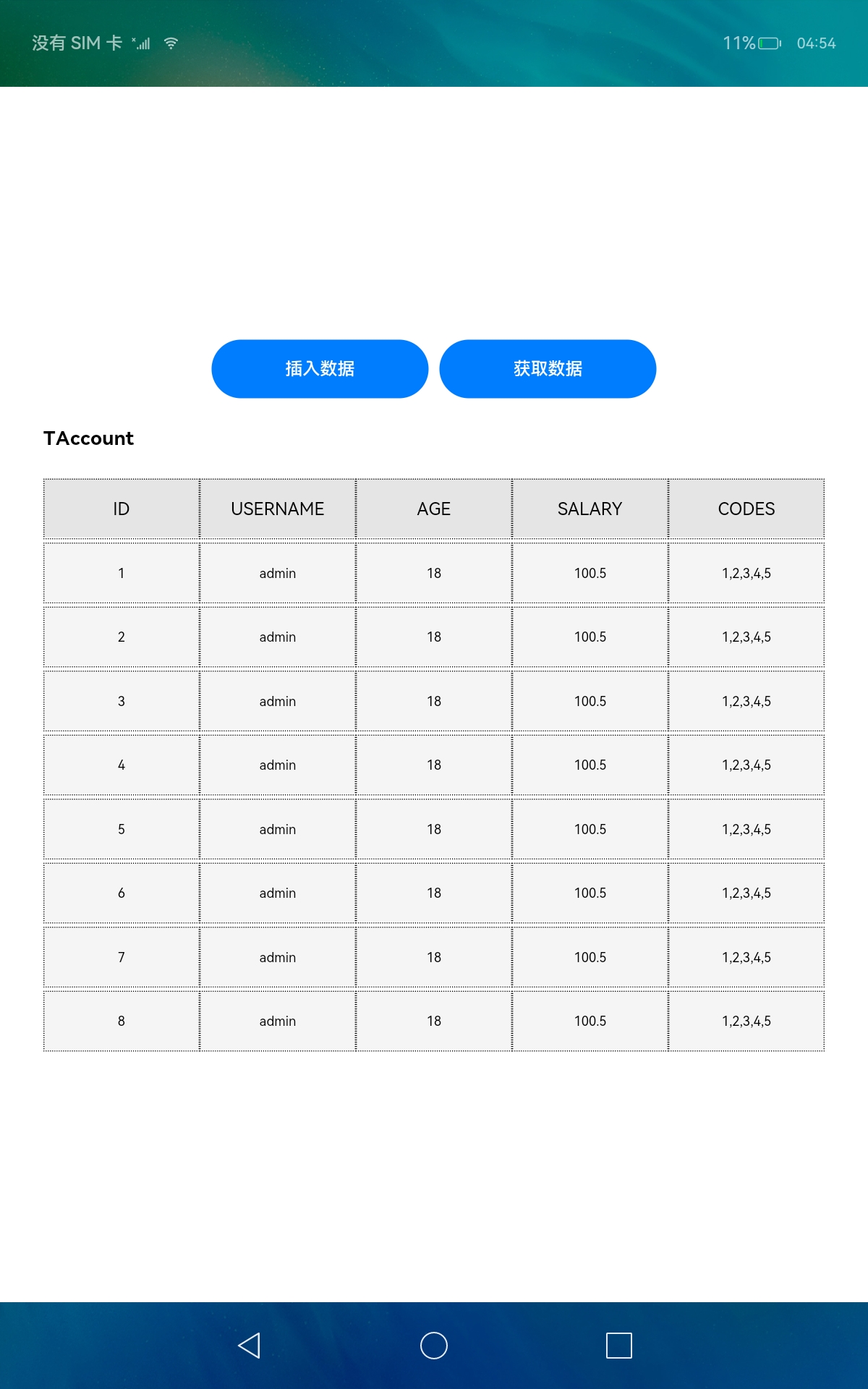
- 頁面顯示
// 顯示表名稱
Text(TableConstants.T_ACCOUNT_NAME)
.fontSize(18)
.fontWeight(700)
.width('90%').height(54)
Column({space: 5}) {
if (this.result !== null) {
// 顯示表字段
GridRow({
columns: TableConstants.T_ACCOUNT_FIELDS.length,
direction: GridRowDirection.Row
}) {
ForEach(this.result.fields, (field) => {
GridCol() {
Text(field)
.width("100%").height(54)
.fontSize(16)
.textAlign(TextAlign.Center)
}
.colStyle()
})
}
.width('90%').height(54)
.backgroundColor(0xE5E5E5)
// 顯示表數(shù)據(jù)
ForEach(this.result.data, (item) => {
GridRow({
columns: TableConstants.T_ACCOUNT_FIELDS.length,
direction: GridRowDirection.Row
}) {
ForEach(TableConstants.T_ACCOUNT_FIELDS, (field) => {
GridCol() {
this.Label(item[field.name].toString())
}
.colStyle()
})
}
.width('90%').height(54)
.backgroundColor(0xF5F5F5)
}, temp => temp.toString())
}
}
.width('100%')
聲明:本文內(nèi)容及配圖由入駐作者撰寫或者入駐合作網(wǎng)站授權轉(zhuǎn)載。文章觀點僅代表作者本人,不代表電子發(fā)燒友網(wǎng)立場。文章及其配圖僅供工程師學習之用,如有內(nèi)容侵權或者其他違規(guī)問題,請聯(lián)系本站處理。
舉報投訴
-
數(shù)據(jù)庫
+關注
關注
7文章
3900瀏覽量
65732 -
關系型數(shù)據(jù)庫
+關注
關注
0文章
8瀏覽量
2390 -
OpenHarmony
+關注
關注
26文章
3818瀏覽量
18093
發(fā)布評論請先 登錄
相關推薦
熱點推薦
HarmonyOS開發(fā)案例:【搭建關系型數(shù)據(jù)庫】(4)
本節(jié)將介紹如何調(diào)用關系型數(shù)據(jù)庫接口在本地搭建數(shù)據(jù)庫,并讀寫相應的用戶數(shù)據(jù)。

關系型數(shù)據(jù)庫與非關系數(shù)據(jù)庫的區(qū)別淺析
關系型數(shù)據(jù)庫的一個劣勢就是 阻抗失諧(impedance mismatch):關系模型和內(nèi)存中的數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構之間存在差異
發(fā)表于 06-03 06:03
HarmonyOS關系型數(shù)據(jù)庫和對象關系數(shù)據(jù)庫的使用方法
容易就上手的知識。本篇速成教程直接使用最精準和簡短的文字,再配上講解代碼,讓我們能在10分鐘左右就能掌握最基本的數(shù)據(jù)庫使用方法。數(shù)據(jù)庫的三大要素:數(shù)據(jù)庫、表、字段,接下來為大家介紹關系
發(fā)表于 03-29 14:10
基于數(shù)據(jù)庫查詢過程優(yōu)化設計
在大型關系數(shù)據(jù)庫管理與開發(fā)中,優(yōu)化設計極大地提高數(shù)據(jù)庫的性能。通過對一大型數(shù)據(jù)庫查詢語句執(zhí)行過程的討論,提出了對同一表格進行多個選擇運算的優(yōu)
發(fā)表于 02-27 16:05
?18次下載
數(shù)據(jù)的庫表查詢
庫表查詢一、實驗目的通過基于關系型網(wǎng)絡數(shù)據(jù)庫管理系統(tǒng)SQL Server的上機實驗,使學生進一步了解關系
發(fā)表于 05-10 10:55
?0次下載
什么是非關系型數(shù)據(jù)庫
什么是非關系型數(shù)據(jù)庫
談到非關系型數(shù)據(jù)庫設計的難點,朱海峰說:“我們可以從一些場景來看這個問題
發(fā)表于 06-17 15:49
?3206次閱讀
hbase和關系型數(shù)據(jù)庫的區(qū)別
hbase和關系型數(shù)據(jù)庫的區(qū)別就是對于傳統(tǒng)數(shù)據(jù)庫,增加列對于一個項目來講,改變是非常大的。但是對于nosql,插入列和刪除列,跟傳統(tǒng)數(shù)據(jù)庫里
發(fā)表于 12-27 15:51
?1.2w次閱讀
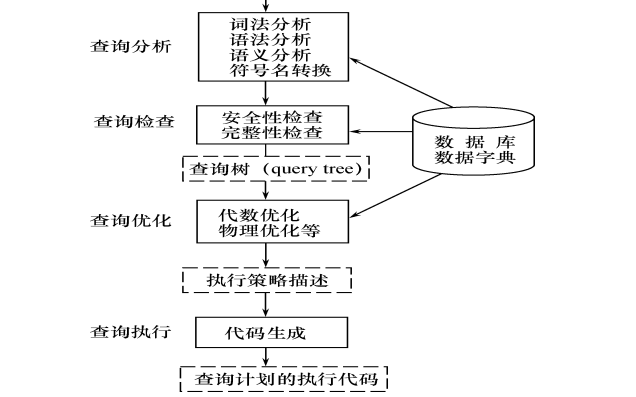
數(shù)據(jù)庫系統(tǒng)概論之如何進行關系查詢處理和查詢優(yōu)化
本文檔的主要內(nèi)容詳細介紹的是數(shù)據(jù)庫系統(tǒng)概論之如何進行關系查詢處理和查詢優(yōu)化主要內(nèi)容包括了:1、關系數(shù)據(jù)庫系統(tǒng)的
發(fā)表于 11-15 15:12
?11次下載
數(shù)據(jù)庫原理的關系代數(shù)詳細講解
關系代數(shù)與關系數(shù)據(jù)庫操作
關系代數(shù)是關系數(shù)據(jù)庫系統(tǒng)查詢語言的理論基礎。
發(fā)表于 10-31 11:53
?5次下載
OpenHarmony關系型數(shù)據(jù)庫概述
關系型數(shù)據(jù)庫(Relational Database, 以下簡稱RDB)是一種基于關系模型來管理數(shù)據(jù)的數(shù)
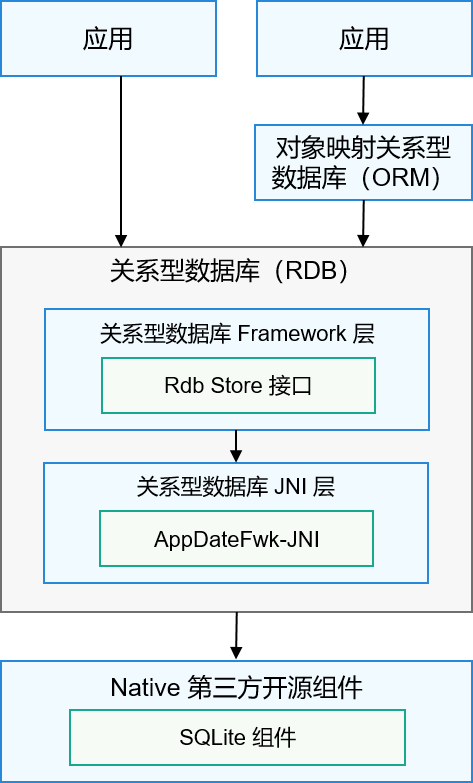
關系型數(shù)據(jù)庫的基本原理(什么是關系型數(shù)據(jù)庫)
組成。關系數(shù)據(jù)庫是基于實用和可重復使用的概念,是支持高性能交互查詢、交易處理能力、安全性和靈活性的關鍵數(shù)據(jù)存儲和維護方法。關系型
python讀取數(shù)據(jù)庫數(shù)據(jù) python查詢數(shù)據(jù)庫 python數(shù)據(jù)庫連接
python讀取數(shù)據(jù)庫數(shù)據(jù) python查詢數(shù)據(jù)庫 python數(shù)據(jù)庫連接 Python是一門高級編程語言,廣泛應用于各種領域。其中,Pyt
關系型數(shù)據(jù)庫和非關系型區(qū)別
關系型數(shù)據(jù)庫和非關系型數(shù)據(jù)庫在多個方面存在顯著差異,主機推薦小編為您整理發(fā)布





 OpenHarmony關系型數(shù)據(jù)庫查詢結(jié)果呈現(xiàn)
OpenHarmony關系型數(shù)據(jù)庫查詢結(jié)果呈現(xiàn)










評論