特征重要性評(píng)分是一種為輸入特征評(píng)分的手段,其依據(jù)是輸入特征在預(yù)測(cè)目標(biāo)變量過(guò)程中的有用程度。
特征重要性有許多類型和來(lái)源,盡管有許多比較常見(jiàn),比如說(shuō)統(tǒng)計(jì)相關(guān)性得分,線性模型的部分系數(shù),基于決策樹(shù)的特征重要性和經(jīng)過(guò)隨機(jī)排序得到重要性得分。
特征重要性在預(yù)測(cè)建模項(xiàng)目中起著重要作用,包括提供對(duì)數(shù)據(jù)、模型的見(jiàn)解,以及如何降維和選擇特征,從而提高預(yù)測(cè)模型的的效率和有效性。
在本教程中,我將會(huì)闡述用于python機(jī)器學(xué)習(xí)的特征重要性。完成本教程后,你將會(huì)知道:
特征重要性在預(yù)測(cè)建模中的作用
如何計(jì)算和查看來(lái)自線性模型和決策樹(shù)的特征重要性
如何計(jì)算和查看隨機(jī)排序重要性得分
現(xiàn)在讓我們開(kāi)始吧。
教程概述
本教程分為五部分,分別是:
1.特征重要性
2.準(zhǔn)備
2.1. 檢查Scikit-Learn版本
2.2. 創(chuàng)建測(cè)試數(shù)據(jù)集
3.特征重要性系數(shù)
3.1. 基于線性回歸系數(shù)的特征重要性
3.2. 基于Logistic回歸的特征重要性
4.基于決策樹(shù)的特征重要性
4.1. 基于CART的特征重要性
4.2. 基于隨機(jī)森林的特征重要性
4.3. 基于XGBoost的特征重要性
5.隨機(jī)排序特征重要性
5.1. 隨機(jī)排序(回歸)中的特征重要性
5.2. 隨機(jī)排序(分類)中的特征重要性
1.特征重要性
特征重要性是一種為預(yù)測(cè)模型的輸入特征評(píng)分的方法,該方法揭示了進(jìn)行預(yù)測(cè)時(shí)每個(gè)特征的相對(duì)重要性。
可以為涉及預(yù)測(cè)數(shù)值的問(wèn)題(稱為回歸)和涉及預(yù)測(cè)類別標(biāo)簽的問(wèn)題(稱為分類)計(jì)算特征重要性得分。
這些得分非常有用,可用于預(yù)測(cè)建模問(wèn)題中的多種情況,例如:
更好地理解數(shù)據(jù)
更好地理解模型
減少輸入特征的數(shù)量
特征重要性得分可以幫助了解數(shù)據(jù)集
相對(duì)得分可以突出顯示哪些特征可能與目標(biāo)最相關(guān),反之則突出哪些特征最不相關(guān)。這可以由一個(gè)領(lǐng)域?qū)<医忉專⑶铱梢杂米魇占嗟幕虿煌臄?shù)據(jù)的基礎(chǔ)。
特征重要性得分可以幫助了解模型
大多數(shù)重要性得分是通過(guò)數(shù)據(jù)集擬合出的預(yù)測(cè)模型計(jì)算的。查看重要性得分可以洞悉該特定模型,以及知道在進(jìn)行預(yù)測(cè)時(shí)哪些特征最重要和哪些最不重要。這是一種模型解釋,適用于那些支持它的模型。
特征重要性可用于改進(jìn)預(yù)測(cè)模型
可以使用的重要性得分來(lái)選擇要?jiǎng)h除的特征(最低得分)或要保留的特征(最高得分)。這是一種特征選擇,可以簡(jiǎn)化正在建模的問(wèn)題,加快建模過(guò)程(刪除特征稱為降維),在某些情況下,還可以改善模型的性能。
特征重要性得分可以被輸入到包裝器模型,如SelectFromModel或SelectKBest,以進(jìn)行特征選擇。
有許多方法和模型可以計(jì)算特征重要性得分。
也許最簡(jiǎn)單的方法是計(jì)算每個(gè)特征和目標(biāo)變量之間的統(tǒng)計(jì)學(xué)相關(guān)系數(shù)。
在本教程中,我們將研究三種比較高級(jí)的特征重要性,即:
從模型系數(shù)得知的特征重要性。
決策樹(shù)中的特征重要性。
隨機(jī)排序檢驗(yàn)中的特征重要性。
現(xiàn)在讓我們深入了解這三個(gè)!
2.準(zhǔn)備
在深入學(xué)習(xí)之前,我們先確認(rèn)我們的環(huán)境并準(zhǔn)備一些測(cè)試數(shù)據(jù)集。
檢查Scikit-Learn版本
首先,確認(rèn)你已安裝最新版本的scikit-learn庫(kù)。這非常重要,因?yàn)樵诒窘坛讨校覀兾覀冄芯康囊恍┠P托枰钚掳娴膸?kù)。
您可以使用以下示例代碼來(lái)查看已安裝的庫(kù)的版本:
# check scikit-learn version
import sklearn
print(sklearn.__version__)
運(yùn)行示例代碼將會(huì)打印出庫(kù)的版本。在撰寫(xiě)本文時(shí),大概是version 0.22。你需要使用此版本或更高版本的scikit-learn。
0.22.1
生成測(cè)試數(shù)據(jù)集
接下來(lái),讓我們生成一些測(cè)試數(shù)據(jù)集,這些數(shù)據(jù)集可以作為基礎(chǔ)來(lái)證明和探索特征重要性得分。每個(gè)測(cè)試問(wèn)題有五個(gè)重要特征和五不重要的特征,看看哪種方法可以根據(jù)其重要性找到或區(qū)分特征可能會(huì)比較有意思。
分類數(shù)據(jù)集
我們將使用make_classification()函數(shù)創(chuàng)建一個(gè)用于測(cè)試的二進(jìn)制分類數(shù)據(jù)集。
數(shù)據(jù)集將包含1000個(gè)實(shí)例,且包含10個(gè)輸入特征,其中五個(gè)將會(huì)提供信息,其余五個(gè)是多余的。
為了確保每次運(yùn)行代碼時(shí)都得到相同的實(shí)例,我們將使用假隨機(jī)數(shù)種子。下面列出了創(chuàng)建數(shù)據(jù)集的示例。
# test classification dataset
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
# define dataset
X, y = make_classification(n_samples=1000, n_features=10, n_informative=5, n_redundant=5, random_state=1)
# summarize the dataset
print(X.shape, y.shape)
運(yùn)行示例,創(chuàng)建數(shù)據(jù)集,并確保所需的樣本和特征數(shù)量。
(1000, 10) (1000,)
回歸數(shù)據(jù)集
我們將使用make_regression()函數(shù)創(chuàng)建一個(gè)用于測(cè)試的回歸數(shù)據(jù)集。
像分類數(shù)據(jù)集一樣,回歸數(shù)據(jù)集將包含1000個(gè)實(shí)例,且包含10個(gè)輸入特征,其中五個(gè)將會(huì)提供信息,其余五個(gè)是多余的。
# test regression dataset
from sklearn.datasets import make_regression
# define dataset
X, y = make_regression(n_samples=1000, n_features=10, n_informative=5, random_state=1)
# summarize the dataset
print(X.shape, y.shape)
運(yùn)行示例,創(chuàng)建數(shù)據(jù)集,并確保所需的樣本和特征數(shù)量。
(1000, 10) (1000,)
接下來(lái),我們仔細(xì)看一下特征重要性系數(shù)。
3.特征重要性系數(shù)
線性的機(jī)器學(xué)習(xí)能夠擬合出預(yù)測(cè)是輸入值的加權(quán)和的模型。
案例包括線性回歸,邏輯回歸,和正則化的擴(kuò)展案例,如嶺回歸和彈性網(wǎng)絡(luò)。
所有這些算法都是找到一組要在加權(quán)求和中使用的系數(shù),以便進(jìn)行預(yù)測(cè)。這些系數(shù)可以直接用作粗略類型的特征重要性得分。
我們來(lái)仔細(xì)研究一下分類和回歸中的特征重要性系數(shù)。我們將在數(shù)據(jù)集中擬合出一個(gè)模型以找到系數(shù),然后計(jì)算每個(gè)輸入特征的重要性得分,最終創(chuàng)建一個(gè)條形圖來(lái)了解特征的相對(duì)重要性。
3.1線性回歸特征重要性
我們可以在回歸數(shù)據(jù)集中擬合出一個(gè)LinearRegression模型,并檢索coeff_屬性,該屬性包含為每個(gè)輸入變量(特征)找到的系數(shù)。這些系數(shù)可以為粗略特征重要性評(píng)分提供依據(jù)。該模型假設(shè)輸入變量具有相同的比例或者在擬合模型之前已被按比例縮放。
下面列出了針對(duì)特征重要性的線性回歸系數(shù)的完整示例。
# linear regression feature importance
from sklearn.datasets import make_regression
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from matplotlib import pyplot
# define dataset
X, y = make_regression(n_samples=1000, n_features=10, n_informative=5, random_state=1)
# define the model
model = LinearRegression()
# fit the model
model.fit(X, y)
# get importance
importance = model.coef_
# summarize feature importance
for i,v in enumerate(importance):
print(‘Feature: %0d, Score: %.5f’ % (i,v))
# plot feature importance
pyplot.bar([x for x in range(len(importance))], importance)
pyplot.show()
運(yùn)行示例,擬合模型,然后輸出每個(gè)特征的系數(shù)值。
得分表明,模型找到了五個(gè)重要特征,并用零標(biāo)記了剩下的特征,實(shí)際上,將他們從模型中去除了。
Feature: 0, Score: 0.00000
Feature: 1, Score: 12.44483
Feature: 2, Score: -0.00000
Feature: 3, Score: -0.00000
Feature: 4, Score: 93.32225
Feature: 5, Score: 86.50811
Feature: 6, Score: 26.74607
Feature: 7, Score: 3.28535
Feature: 8, Score: -0.00000
Feature: 9, Score: 0.00000
然后為特征重要性得分創(chuàng)建條形圖。

這種方法也可以用于嶺回歸和彈性網(wǎng)絡(luò)模型。
3.2 Logistic回歸特征重要性
就像線性回歸模型一樣,我們也可以在回歸數(shù)據(jù)集中擬合出一個(gè)LogisticRegression模型,并檢索coeff_屬性。這些系數(shù)可以為粗略特征重要性評(píng)分提供依據(jù)。該模型假設(shè)輸入變量具有相同的比例或者在擬合模型之前已被按比例縮放。
下面列出了針對(duì)特征重要性的Logistic回歸系數(shù)的完整示例。
# logistic regression for feature importance
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from matplotlib import pyplot
# define dataset
X, y = make_classification(n_samples=1000, n_features=10, n_informative=5, n_redundant=5, random_state=1)
# define the model
model = LogisticRegression()
# fit the model
model.fit(X, y)
# get importance
importance = model.coef_[0]
# summarize feature importance
for i,v in enumerate(importance):
print(‘Feature: %0d, Score: %.5f’ % (i,v))
# plot feature importance
pyplot.bar([x for x in range(len(importance))], importance)
pyplot.show()
運(yùn)行示例,擬合模型,然后輸出每個(gè)特征的系數(shù)值。
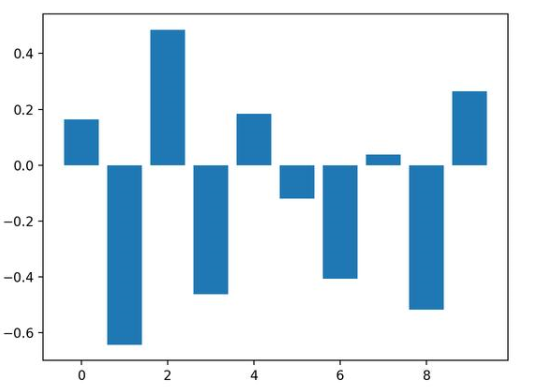
回想一下,這是有關(guān)0和1的分類問(wèn)題。請(qǐng)注意系數(shù)既可以為正,也可以為負(fù)。正數(shù)表示預(yù)測(cè)類別1的特征,而負(fù)數(shù)表示預(yù)測(cè)類別0的特征。
從這些結(jié)果,至少?gòu)奈宜赖慕Y(jié)果中,無(wú)法清晰的確定出重要和不重要特征。
Feature: 0, Score: 0.16320
Feature: 1, Score: -0.64301
Feature: 2, Score: 0.48497
Feature: 3, Score: -0.46190
Feature: 4, Score: 0.18432
Feature: 5, Score: -0.11978
Feature: 6, Score: -0.40602
Feature: 7, Score: 0.03772
Feature: 8, Score: -0.51785
Feature: 9, Score: 0.26540
然后為特征重要性得分創(chuàng)建條形圖。
現(xiàn)在我們已經(jīng)看到了將系數(shù)用作重要性得分的示例,接下來(lái)讓我們看向基于決策樹(shù)的重要性得分的常見(jiàn)示例
4.基于決策樹(shù)的特征重要性
決策樹(shù)算法,比如說(shuō)classification and regression trees(CART)根據(jù)Gini系數(shù)或熵的減少來(lái)提供重要性得分。這個(gè)方法也可用于隨機(jī)森林和梯度提升算法。
OK.現(xiàn)在讓我們看看相應(yīng)的運(yùn)行示例。
4.1基于CART的特征重要性
對(duì)于在scikit-learn中實(shí)現(xiàn)的特征重要性,我們可以將CART算法用于DecisionTreeRegressor和DecisionTreeClassifier類
擬合后,模型提供feature_importances_屬性,可以訪問(wèn)該屬性以檢索每個(gè)輸入特征的相對(duì)重要性得分。
讓我們看一個(gè)用于回歸和分類的示例。
基于CART(回歸)的特征重要性
下面列出了擬合DecisionTreeRegressor和計(jì)算特征重要性得分的完整示例。
# decision tree for feature importance on a regression problem
from sklearn.datasets import make_regression
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeRegressor
from matplotlib import pyplot
# define dataset
X, y = make_regression(n_samples=1000, n_features=10, n_informative=5, random_state=1)
# define the model
model = DecisionTreeRegressor()
# fit the model
model.fit(X, y)
# get importance
importance = model.feature_importances_
# summarize feature importance
for i,v in enumerate(importance):
print(‘Feature: %0d, Score: %.5f’ % (i,v))
# plot feature importance
pyplot.bar([x for x in range(len(importance))], importance)
pyplot.show()
運(yùn)行示例,擬合模型,然后輸出每個(gè)特征的系數(shù)值。
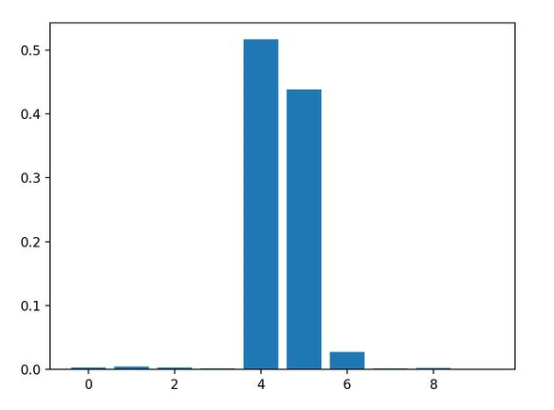
結(jié)果表明,這十個(gè)特征中的三個(gè)可能對(duì)預(yù)測(cè)很重要。
Feature: 0, Score: 0.00294
Feature: 1, Score: 0.00502
Feature: 2, Score: 0.00318
Feature: 3, Score: 0.00151
Feature: 4, Score: 0.51648
Feature: 5, Score: 0.43814
Feature: 6, Score: 0.02723
Feature: 7, Score: 0.00200
Feature: 8, Score: 0.00244
Feature: 9, Score: 0.00106
然后為特征重要性得分創(chuàng)建條形圖。
基于CART(分類)的特征重要性
下面列出了擬合DecisionTreeClassifier和計(jì)算特征重要性得分的完整示例
# decision tree for feature importance on a classification problem
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from matplotlib import pyplot
# define dataset
X, y = make_classification(n_samples=1000, n_features=10, n_informative=5, n_redundant=5, random_state=1)
# define the model
model = DecisionTreeClassifier()
# fit the model
model.fit(X, y)
# get importance
importance = model.feature_importances_
# summarize feature importance
for i,v in enumerate(importance):
print(‘Feature: %0d, Score: %.5f’ % (i,v))
# plot feature importance
pyplot.bar([x for x in range(len(importance))], importance)
pyplot.show()
運(yùn)行示例,擬合模型,然后輸出每個(gè)特征的系數(shù)值。
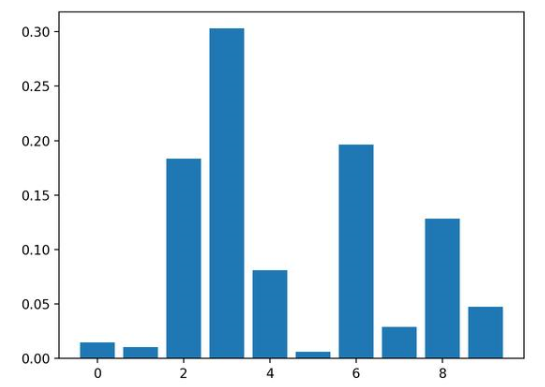
結(jié)果表明,這十個(gè)特征中的四個(gè)可能對(duì)預(yù)測(cè)很重要。
Feature: 0, Score: 0.01486
Feature: 1, Score: 0.01029
Feature: 2, Score: 0.18347
Feature: 3, Score: 0.30295
Feature: 4, Score: 0.08124
Feature: 5, Score: 0.00600
Feature: 6, Score: 0.19646
Feature: 7, Score: 0.02908
Feature: 8, Score: 0.12820
Feature: 9, Score: 0.04745
然后為特征重要性得分創(chuàng)建條形圖。
4.2隨機(jī)森林中的特征重要性
對(duì)于在scikit-learn中實(shí)現(xiàn)的特征重要性,我們可以將Random Forest算法用于DecisionTreeRegressor和DecisionTreeClassifier類。
擬合后,模型提供feature_importances_屬性,可以訪問(wèn)該屬性以檢索每個(gè)輸入特征的相對(duì)重要性得分。
這種方法也可以與裝袋和極端隨機(jī)樹(shù)(extraTree)算法一起使用。
讓我們看一個(gè)用于回歸和分類的示例。
隨機(jī)森林(回歸)中的特征重要性
下面列出了擬合RandomForestRegressor和計(jì)算特征重要性得分的完整示例
# random forest for feature importance on a regression problem
from sklearn.datasets import make_regression
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor
from matplotlib import pyplot
# define dataset
X, y = make_regression(n_samples=1000, n_features=10, n_informative=5, random_state=1)
# define the model
model = RandomForestRegressor()
# fit the model
model.fit(X, y)
# get importance
importance = model.feature_importances_
# summarize feature importance
for i,v in enumerate(importance):
print(‘Feature: %0d, Score: %.5f’ % (i,v))
# plot feature importance
pyplot.bar([x for x in range(len(importance))], importance)
pyplot.show()
運(yùn)行示例,擬合模型,然后輸出每個(gè)特征的系數(shù)值。
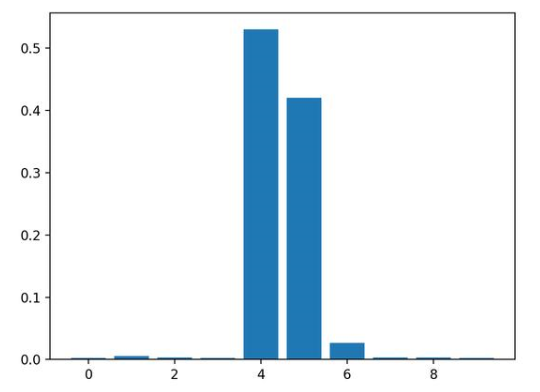
結(jié)果表明,這十個(gè)特征中的兩個(gè)或三個(gè)可能對(duì)預(yù)測(cè)很重要。
Feature: 0, Score: 0.00280
Feature: 1, Score: 0.00545
Feature: 2, Score: 0.00294
Feature: 3, Score: 0.00289
Feature: 4, Score: 0.52992
Feature: 5, Score: 0.42046
Feature: 6, Score: 0.02663
Feature: 7, Score: 0.00304
Feature: 8, Score: 0.00304
Feature: 9, Score: 0.00283
然后為特征重要性得分創(chuàng)建條形圖。
隨機(jī)森林(分類)中的特征重要性
下面列出了擬合RandomForestClassifier和計(jì)算特征重要性得分的完整示例
# random forest for feature importance on a classification problem
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from matplotlib import pyplot
# define dataset
X, y = make_classification(n_samples=1000, n_features=10, n_informative=5, n_redundant=5, random_state=1)
# define the model
model = RandomForestClassifier()
# fit the model
model.fit(X, y)
# get importance
importance = model.feature_importances_
# summarize feature importance
for i,v in enumerate(importance):
print(‘Feature: %0d, Score: %.5f’ % (i,v))
# plot feature importance
pyplot.bar([x for x in range(len(importance))], importance)
pyplot.show()
運(yùn)行示例,擬合模型,然后輸出每個(gè)特征的系數(shù)值。
結(jié)果表明,這十個(gè)特征中的兩個(gè)或三個(gè)可能對(duì)預(yù)測(cè)很重要。
Feature: 0, Score: 0.06523
Feature: 1, Score: 0.10737
Feature: 2, Score: 0.15779
Feature: 3, Score: 0.20422
Feature: 4, Score: 0.08709
Feature: 5, Score: 0.09948
Feature: 6, Score: 0.10009
Feature: 7, Score: 0.04551
Feature: 8, Score: 0.08830
Feature: 9, Score: 0.04493
然后為特征重要性得分創(chuàng)建條形圖。
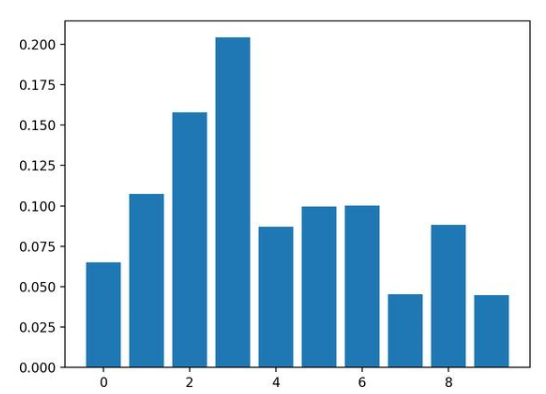
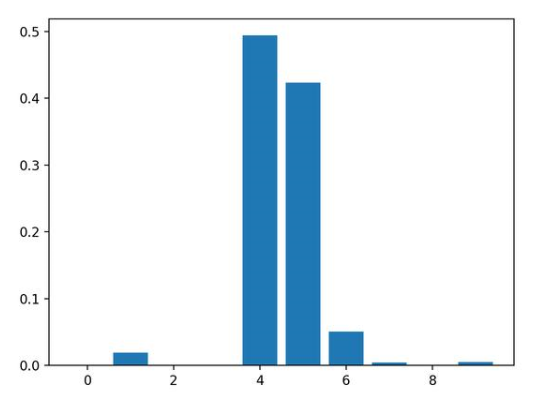
4.3基于XGBoost的特征重要性
XGBoost是一個(gè)庫(kù),它提供了隨機(jī)梯度提升算法的高效實(shí)現(xiàn)。可以通過(guò)XGBRegressor和XGBClassifier類將此算法與scikit-learn一起使用。
擬合后,模型提供feature_importances_屬性,可以訪問(wèn)該屬性以檢索每個(gè)輸入特征的相對(duì)重要性得分。
scikit-learn還通過(guò)GradientBoostingClassifier和GradientBoostingRegressor提供了該算法,并且可以使用相同的特征選擇方法
首先,安裝XGBoost庫(kù),例如:
sudo pip install xgboost
然后,通過(guò)檢查版本號(hào)來(lái)確認(rèn)該庫(kù)已正確安裝并且可以正常工作。
# check xgboost version
import xgboost
print(xgboost.__version__)
運(yùn)行該示例,你應(yīng)該看到以下版本號(hào)或者更高版本。
0.90
有關(guān)XGBoost庫(kù)的更多信息,請(qǐng)看:
XGBoost with Python
讓我們看一個(gè)用于回歸和分類問(wèn)題的示例。
基于XGBoost(回歸)的特征重要性
下面列出了擬合XGBRegressor并且計(jì)算特征重要性得分的完整示例
# xgboost for feature importance on a regression problem
from sklearn.datasets import make_regression
from xgboost import XGBRegressor
from matplotlib import pyplot
# define dataset
X, y = make_regression(n_samples=1000, n_features=10, n_informative=5, random_state=1)
# define the model
model = XGBRegressor()
# fit the model
model.fit(X, y)
# get importance
importance = model.feature_importances_
# summarize feature importance
for i,v in enumerate(importance):
print(‘Feature: %0d, Score: %.5f’ % (i,v))
# plot feature importance
pyplot.bar([x for x in range(len(importance))], importance)
pyplot.show()
運(yùn)行示例,擬合模型,然后輸出每個(gè)特征的系數(shù)值。
結(jié)果表明,這十個(gè)特征中的兩個(gè)或三個(gè)可能對(duì)預(yù)測(cè)很重要。
Feature: 0, Score: 0.00060
Feature: 1, Score: 0.01917
Feature: 2, Score: 0.00091
Feature: 3, Score: 0.00118
Feature: 4, Score: 0.49380
Feature: 5, Score: 0.42342
Feature: 6, Score: 0.05057
Feature: 7, Score: 0.00419
Feature: 8, Score: 0.00124
Feature: 9, Score: 0.00491
然后為特征重要性得分創(chuàng)建條形圖。
基于XGBoost(分類)的特征重要性
下面列出了擬合XGBClassifier并且計(jì)算特征重要性得分的完整示例
# xgboost for feature importance on a classification problem
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
from xgboost import XGBClassifier
from matplotlib import pyplot
# define dataset
X, y = make_classification(n_samples=1000, n_features=10, n_informative=5, n_redundant=5, random_state=1)
# define the model
model = XGBClassifier()
# fit the model
model.fit(X, y)
# get importance
importance = model.feature_importances_
# summarize feature importance
for i,v in enumerate(importance):
print(‘Feature: %0d, Score: %.5f’ % (i,v))
# plot feature importance
pyplot.bar([x for x in range(len(importance))], importance)
pyplot.show()
運(yùn)行示例,擬合模型,然后輸出每個(gè)特征的系數(shù)值。
結(jié)果表明,這十個(gè)特征中有七個(gè)可能對(duì)預(yù)測(cè)很重要。
Feature: 0, Score: 0.02464
Feature: 1, Score: 0.08153
Feature: 2, Score: 0.12516
Feature: 3, Score: 0.28400
Feature: 4, Score: 0.12694
Feature: 5, Score: 0.10752
Feature: 6, Score: 0.08624
Feature: 7, Score: 0.04820
Feature: 8, Score: 0.09357
Feature: 9, Score: 0.02220
然后為特征重要性得分創(chuàng)建條形圖。
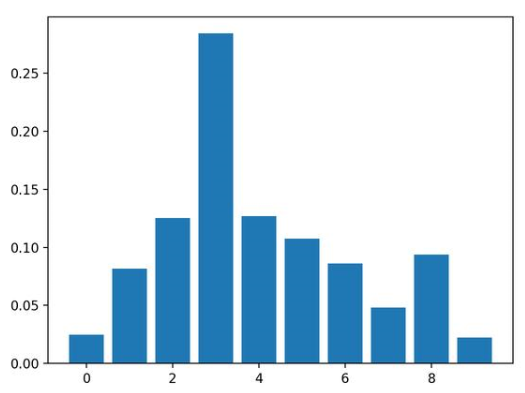
5.基于隨機(jī)排序的特征重要性
隨機(jī)排序特征重要性(Permutation feature importance)可以計(jì)算相對(duì)重要性,與所使用的模型無(wú)關(guān)。
首先,在數(shù)據(jù)集中擬合出一個(gè)模型,比如說(shuō)一個(gè)不支持本地特征重要性評(píng)分的模型。然后,盡管對(duì)數(shù)據(jù)集中的特征值進(jìn)行了干擾,但仍可以使用該模型進(jìn)行預(yù)測(cè)。對(duì)數(shù)據(jù)集中的每個(gè)特征進(jìn)行此操作。然后,再將整個(gè)流程重新操作3、5、10或更多次。我們得到每個(gè)輸入特征的平均重要性得分(以及在重復(fù)的情況下得分的分布)。
此方法可以用于回歸或分類,要求選擇性能指標(biāo)作為重要性得分的基礎(chǔ),例如回歸中的均方誤差和分類中的準(zhǔn)確性。
可以通過(guò)permutation_importance()函數(shù)(以模型和數(shù)據(jù)集為參數(shù))和評(píng)分函數(shù)進(jìn)行隨機(jī)排序特性選擇。
讓我們看下這個(gè)特征選擇方法,其算法并不支持特征選擇,尤其是k近鄰算法( k-nearest neighbors)。
5.1隨機(jī)排序(回歸)特征重要性
下面列出了擬合KNeighborsRegressor并且計(jì)算特征重要性得分的完整示例。
# permutation feature importance with knn for regression
from sklearn.datasets import make_regression
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsRegressor
from sklearn.inspection import permutation_importance
from matplotlib import pyplot
# define dataset
X, y = make_regression(n_samples=1000, n_features=10, n_informative=5, random_state=1)
# define the model
model = KNeighborsRegressor()
# fit the model
model.fit(X, y)
# perform permutation importance
results = permutation_importance(model, X, y, scoring=‘neg_mean_squared_error’)
# get importance
importance = results.importances_mean
# summarize feature importance
for i,v in enumerate(importance):
print(‘Feature: %0d, Score: %.5f’ % (i,v))
# plot feature importance
pyplot.bar([x for x in range(len(importance))], importance)
pyplot.show()
運(yùn)行示例,擬合模型,然后輸出每個(gè)特征的系數(shù)值。
結(jié)果表明,這十個(gè)特征中的兩個(gè)或三個(gè)可能對(duì)預(yù)測(cè)很重要。
Feature: 0, Score: 175.52007
Feature: 1, Score: 345.80170
Feature: 2, Score: 126.60578
Feature: 3, Score: 95.90081
Feature: 4, Score: 9666.16446
Feature: 5, Score: 8036.79033
Feature: 6, Score: 929.58517
Feature: 7, Score: 139.67416
Feature: 8, Score: 132.06246
Feature: 9, Score: 84.94768
然后為特征重要性得分創(chuàng)建條形圖。
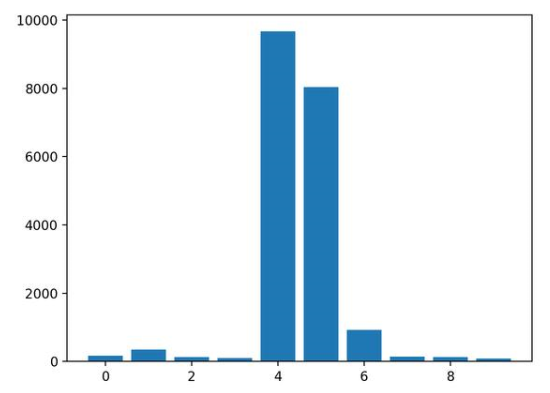
5.2隨機(jī)排序(分類)特征重要性
下面列出了擬合KNeighborsClassifier并且計(jì)算特征重要性得分的完整示例。
# permutation feature importance with knn for classification
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
from sklearn.inspection import permutation_importance
from matplotlib import pyplot
# define dataset
X, y = make_classification(n_samples=1000, n_features=10, n_informative=5, n_redundant=5, random_state=1)
# define the model
model = KNeighborsClassifier()
# fit the model
model.fit(X, y)
# perform permutation importance
results = permutation_importance(model, X, y, scoring=‘accuracy’)
# get importance
importance = results.importances_mean
# summarize feature importance
for i,v in enumerate(importance):
print(‘Feature: %0d, Score: %.5f’ % (i,v))
# plot feature importance
pyplot.bar([x for x in range(len(importance))], importance)
pyplot.show()
運(yùn)行示例,擬合模型,然后輸出每個(gè)特征的系數(shù)值。
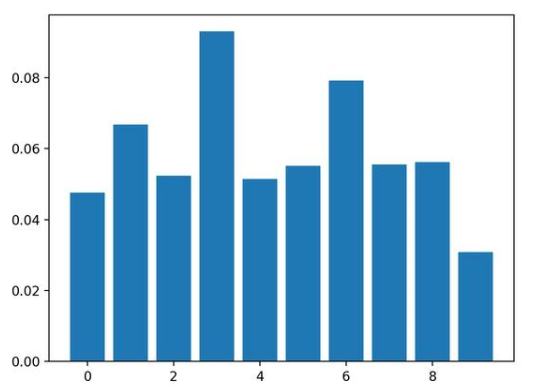
結(jié)果表明,這十個(gè)特征中的兩個(gè)或三個(gè)可能對(duì)預(yù)測(cè)很重要。
Feature: 0, Score: 0.04760
Feature: 1, Score: 0.06680
Feature: 2, Score: 0.05240
Feature: 3, Score: 0.09300
Feature: 4, Score: 0.05140
Feature: 5, Score: 0.05520
Feature: 6, Score: 0.07920
Feature: 7, Score: 0.05560
Feature: 8, Score: 0.05620
Feature: 9, Score: 0.03080
然后為特征重要性得分創(chuàng)建條形圖。
總結(jié)
在本教程中,您知道了在Python機(jī)器學(xué)習(xí)中的特征重要性得分。
具體來(lái)說(shuō),您了解到:
特征重要性在預(yù)測(cè)建模問(wèn)題中的作用
如何從線性模型和決策樹(shù)中計(jì)算和查看特征重要性
如何計(jì)算和查看隨機(jī)排序特征重要性得分
-
代碼
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
30文章
4886瀏覽量
70217 -
數(shù)據(jù)集
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
4文章
1222瀏覽量
25264 -
網(wǎng)絡(luò)模型
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
0文章
44瀏覽量
8687
發(fā)布評(píng)論請(qǐng)先 登錄
工業(yè)中使用哪種計(jì)算機(jī)?






 如何用Python計(jì)算機(jī)器學(xué)習(xí)中特征的重要程度?
如何用Python計(jì)算機(jī)器學(xué)習(xí)中特征的重要程度?










評(píng)論