在之前已經(jīng)通過手寫的方式實(shí)現(xiàn)了一個(gè)詞法分析器,現(xiàn)在,我將利用之前手寫的詞法分析器,使用遞歸下降的方式,實(shí)現(xiàn)一個(gè)簡單的語法分析器。
首先看看實(shí)驗(yàn)要求:
用遞歸下降法編寫一個(gè)語法分析程序,使之與詞法分析器結(jié)合,能夠根據(jù)語言的上下文無關(guān)文法,識別輸入的單詞序列是否文法的句子。
為減輕實(shí)驗(yàn)編程負(fù)擔(dān),這里只要求實(shí)現(xiàn)部分產(chǎn)生式,文法的開始符號為 program 。

第一步,消除左遞歸。觀察上面各個(gè)產(chǎn)生式,出現(xiàn)左遞歸的地方有expr和term。

針對以上式子,首先提取左因子:

消除左遞歸:

觀察到 在if語句處也存在左公因子,一并提取,最終文法定義為:

定義好文法后,考慮詞法分析與語法分析的接口,由于采用遞歸下降的分析過程中,存在對token的回溯操作,因此,每次逐個(gè)獲取詞法單元并不容易實(shí)現(xiàn),考慮將token對應(yīng)的標(biāo)志和內(nèi)容使用pair的數(shù)組保存下來。
pair<int, string> tokens[10000];
int cursor_;
int tokens_size_;
并使用cursor_記錄當(dāng)前準(zhǔn)備分析的位置,通過移動(dòng)cursor_實(shí)現(xiàn)對token串的回溯過程。然后根據(jù)每一條語句,寫出對應(yīng)的梯度下降遞歸函數(shù),就可以完成本實(shí)驗(yàn),使用yylex自動(dòng)生成的方法也類似,只需要維護(hù)tokens數(shù)組即可。
// 工具函數(shù):獲得一個(gè)向前看,但并不移動(dòng)指針
pair<int, string> get_ahead(){
return tokens[cursor_];
}
// 工具函數(shù):嘗試匹配一個(gè)類型,匹配返回真
bool match(int type){
if(cursor_ >= tokens_size_) return false;
if(tokens[cursor_].first == type)
{
cursor_ ++;
return true;
}
return false;
}
// 工具函數(shù):嘗試匹配一個(gè)類型和字符串,都匹配返回真
bool match(int type, string target){
if(tokens[cursor_].first == type && tokens[cursor_].second == target)
{
cursor_ ++;
return true;
}
return false;
}
bool factor(){
cout << "Try to match factor" << endl;
if(match(IDENTITY)) return true;
if(match(DIGIT)) return true;
return match(SYMBOL, "(") && expr() && match(SYMBOL, ")");
}
bool B3(){
cout << "Try to match B3" << endl;
return match(SYMBOL, "%") && factor();
}
bool B2(){
cout << "Try to match B2" << endl;
return match(SYMBOL, "/") && factor();
}
bool B1(){
cout << "Try to match B1" << endl;
return match(SYMBOL, "*") && factor();
}
bool B(){
cout << "Try to match B" << endl;
int backup_cursor = cursor_;
if(B1()) return true;
cursor_ = backup_cursor;
if(B2()) return true;
cursor_ = backup_cursor;
if(B3()) return true;
cursor_ = backup_cursor;
return false;
}
bool D(){
cout << "Try to match D" << endl;
pair<int, string> ahead = get_ahead();
if(ahead.first == SYMBOL && (ahead.second == "*" || ahead.second == "/" || ahead.second == "%")) return B() && D();
return true;
}
bool term(){
cout << "Try to match term" << endl;
return factor() && D();
}
bool A2(){
cout << "Try to match A2" << endl;
return match(SYMBOL, "-") && term();
}
bool A1(){
cout << "Try to match A1" << endl;
return match(SYMBOL, "+") && term();
}
bool A(){
cout << "Try to match A" << endl;
int backup_cursor = cursor_;
if(A1()) return true;
cursor_ = backup_cursor;
if(A2()) return true;
cursor_ = backup_cursor;
return false;
}
bool C(){
cout << "Try to match C" << endl;
pair<int, string> ahead = get_ahead();
if(ahead.first == SYMBOL && (ahead.second == "+" || ahead.second == "-")) return A() && C();
return true;
}
bool expr(){
cout << "Try to match expr" << endl;
return term() && C();
}
bool F(){
cout << "Try to match F" << endl;
pair<int, string> ahead = get_ahead();
if(ahead.first == RELOP) return match(RELOP) && expr();
return true;
}
bool bool_(){
cout << "Try to match bool" << endl;
return expr() && F();
}
bool E(){
cout << "Try to match E" << endl;
pair<int, string> ahead = get_ahead();
if(ahead.first == KEYWORD && ahead.second == "else") return match(KEYWORD, "else") && stmt();
return true;
}
bool stmt6(){
cout << "Try to match stmt choice 6" << endl;
return block();
}
bool stmt5(){
cout << "Try to match stmt choice 5" << endl;
return match(KEYWORD, "break") && match(SYMBOL, ";");
}
bool stmt4(){
cout << "Try to match stmt choice 4" << endl;
return match(KEYWORD, "do") && stmt() && match(KEYWORD, "while") && match(SYMBOL, "(") && bool_() && match(SYMBOL, ")") && match(SYMBOL, ";");
}
bool stmt3(){
cout << "Try to match stmt choice 3" << endl;
return match(KEYWORD, "while") && match(SYMBOL, "(") && bool_() && match(SYMBOL, ")") && stmt();
}
bool stmt2(){
cout << "Try to match stmt choice 2" << endl;
return match(KEYWORD, "if") && match(SYMBOL, "(") && bool_() && match(SYMBOL, ")") && stmt() && E();
}
bool stmt1(){
cout << "Try to match stmt choice 1" << endl;
return match(IDENTITY) && match(SYMBOL, "=") && expr() && match(SYMBOL, ";");
}
bool stmt(){
cout << "Try to match stmt" << endl;
int backup_cursor = cursor_; // 指針的回溯
if(stmt1()) return true;
cursor_ = backup_cursor;
if(stmt2()) return true;
cursor_ = backup_cursor;
if(stmt3()) return true;
cursor_ = backup_cursor;
if(stmt4()) return true;
cursor_ = backup_cursor;
if(stmt5()) return true;
cursor_ = backup_cursor;
if(stmt6()) return true;
cursor_ = backup_cursor;
return false;
}
bool stmts(){
cout << "Try to match stmts" << endl;
pair<int, string> ahead = get_ahead();
if(ahead.first == SYMBOL && ahead.second == "}") return true;
else return stmt() && stmts();
}
bool block(){
cout << "Try to match block" << endl;
return match(SYMBOL, "{") && stmts() && match(SYMBOL, "}");
}
bool program(){
cout << "Try to match program" << endl;
return block();
}
由于已經(jīng)高度模塊化,main函數(shù)很簡單:
int main()
{
if(!DFA()) return 0; // 詞法分析
tokens_size_ = cursor_;
cursor_ = 0; // 初始化指針
if(program()) cout << "ACCEPT !" << endl;
else cout << "ERROR !" << endl;
}
測試:
使用實(shí)驗(yàn)指導(dǎo)代碼測試:
input:
{
i = 2;
sum = 0;
while (i <=100) {
sum = sum + i;
i = i + 2;
if(i%5==0) break;
}
}
output:
SYMBOL : {
i = 2;
IDENTITY : i
SYMBOL : =
DIGIT : 2
SYMBOL : ;
sum = 0;
IDENTITY : sum
SYMBOL : =
DIGIT : 0
SYMBOL : ;
KEYWORD : while
SYMBOL : (
IDENTITY : i
RELOP : <=
DIGIT : 100
SYMBOL : )
SYMBOL : {
IDENTITY : sum
SYMBOL : =
IDENTITY : sum
SYMBOL : +
IDENTITY : i
SYMBOL : ;
IDENTITY : i
SYMBOL : =
IDENTITY : i
SYMBOL : +
DIGIT : 2
SYMBOL : ;
KEYWORD : if
SYMBOL : (
IDENTITY : i
SYMBOL : %
DIGIT : 5
RELOP : ==
DIGIT : 0
SYMBOL : )
KEYWORD : break
SYMBOL : ;
SYMBOL : }
SYMBOL : }
Try to match program
Try to match block
Try to match stmts
Try to match stmt
Try to match stmt choice 1
Try to match expr
Try to match term
Try to match factor
Try to match D
Try to match C
Try to match stmts
Try to match stmt
Try to match stmt choice 1
Try to match expr
Try to match term
Try to match factor
Try to match D
Try to match C
Try to match stmts
Try to match stmt
Try to match stmt choice 1
Try to match stmt choice 2
Try to match stmt choice 3
Try to match bool
Try to match expr
Try to match term
Try to match factor
Try to match D
Try to match C
Try to match F
Try to match expr
Try to match term
Try to match factor
Try to match D
Try to match C
Try to match stmt
Try to match stmt choice 1
Try to match stmt choice 2
Try to match stmt choice 3
Try to match stmt choice 4
Try to match stmt choice 5
Try to match stmt choice 6
Try to match block
Try to match stmts
Try to match stmt
Try to match stmt choice 1
Try to match expr
Try to match term
Try to match factor
Try to match D
Try to match C
Try to match A
Try to match A1
Try to match term
Try to match factor
Try to match D
Try to match C
Try to match stmts
Try to match stmt
Try to match stmt choice 1
Try to match expr
Try to match term
Try to match factor
Try to match D
Try to match C
Try to match A
Try to match A1
Try to match term
Try to match factor
Try to match D
Try to match E
Try to match stmts
Try to match stmts
ACCEPT !
最后發(fā)現(xiàn)梯度遞歸函數(shù)已經(jīng)成功地接受了我們的輸入。
-
分析器
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
0文章
93瀏覽量
12656
發(fā)布評論請先 登錄

基于自頂向下技術(shù)的工程機(jī)械Digital Prototyping設(shè)計(jì)方法及應(yīng)用
如何實(shí)現(xiàn)擴(kuò)頻通信調(diào)制器自頂向下的設(shè)計(jì)?
一個(gè)高效的語法分析器生成工具
YACC在ATLAS語言語法分析中的沖突消解研究
網(wǎng)絡(luò)分析器,網(wǎng)絡(luò)分析器原理是什么?
編譯原理實(shí)踐環(huán)節(jié)模擬試題
借助Lex和Yacc進(jìn)行詞法語法分析
通過模塊之間的調(diào)用實(shí)現(xiàn)自頂向下的設(shè)計(jì)
EDA設(shè)計(jì)一般采用自頂向下的模塊化設(shè)計(jì)方法
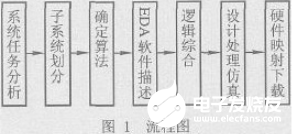





 自頂向下的語法分析器—采用遞歸下降方法
自頂向下的語法分析器—采用遞歸下降方法










評論